Atomistic Monte Carlo simulation of lipid membranes
- PMID: 24469314
- PMCID: PMC3958820
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15021767
Atomistic Monte Carlo simulation of lipid membranes
Abstract
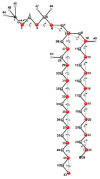
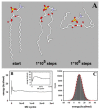
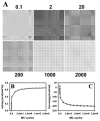
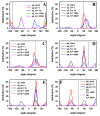
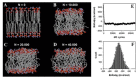
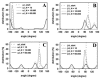
Biological membranes are complex assemblies of many different molecules of which analysis demands a variety of experimental and computational approaches. In this article, we explain challenges and advantages of atomistic Monte Carlo (MC) simulation of lipid membranes. We provide an introduction into the various move sets that are implemented in current MC methods for efficient conformational sampling of lipids and other molecules. In the second part, we demonstrate for a concrete example, how an atomistic local-move set can be implemented for MC simulations of phospholipid monomers and bilayer patches. We use our recently devised chain breakage/closure (CBC) local move set in the bond-/torsion angle space with the constant-bond-length approximation (CBLA) for the phospholipid dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC). We demonstrate rapid conformational equilibration for a single DPPC molecule, as assessed by calculation of molecular energies and entropies. We also show transition from a crystalline-like to a fluid DPPC bilayer by the CBC local-move MC method, as indicated by the electron density profile, head group orientation, area per lipid, and whole-lipid displacements. We discuss the potential of local-move MC methods in combination with molecular dynamics simulations, for example, for studying multi-component lipid membranes containing cholesterol.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A DSC and FTIR spectroscopic study of the effects of the epimeric 4-cholesten-3-ols and 4-cholesten-3-one on the thermotropic phase behaviour and organization of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer membranes: comparison with their 5-cholesten analogues.Chem Phys Lipids. 2014 Jan;177:71-90. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2013.11.008. Epub 2013 Dec 1. Chem Phys Lipids. 2014. PMID: 24296232
-
Combined Monte Carlo and molecular dynamics simulation of hydrated lipid-cholesterol lipid bilayers at low cholesterol concentration.Biophys J. 2001 Mar;80(3):1104-14. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)76088-2. Biophys J. 2001. PMID: 11222276 Free PMC article.
-
Multiscale modeling of lipids and lipid bilayers.Eur Biophys J. 2005 Dec;35(1):53-61. doi: 10.1007/s00249-005-0005-y. Epub 2005 Aug 31. Eur Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 16133633
-
Non-Brownian diffusion in lipid membranes: Experiments and simulations.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Oct;1858(10):2451-2467. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.01.022. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26826272 Review.
-
Molecular modeling of lipid probes and their influence on the membrane.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Oct;1858(10):2353-2361. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.02.014. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26891817 Review.
Cited by
-
Interactions between Beta-2-Glycoprotein-1 and Phospholipid Bilayer-A Molecular Dynamic Study.Membranes (Basel). 2020 Dec 5;10(12):396. doi: 10.3390/membranes10120396. Membranes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33291449 Free PMC article.
-
A review on microfluidic-assisted nanoparticle synthesis, and their applications using multiscale simulation methods.Discov Nano. 2023 Feb 17;18(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s11671-023-03792-x. Discov Nano. 2023. PMID: 36800044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using molecular simulation to understand the skin barrier.Prog Lipid Res. 2022 Nov;88:101184. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101184. Epub 2022 Aug 19. Prog Lipid Res. 2022. PMID: 35988796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Mode Decomposition of Multiphoton and Stimulated Emission Depletion Microscopy Data for Analysis of Fluorescent Probes in Cellular Membranes.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 25;24(7):2096. doi: 10.3390/s24072096. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38610307 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Method for Realistically Simulating the Deposition of Thin Films from the Gas Phase and its Application to Study the Growth of Thin Gold Film on Crystalline Silicon.J Chem Theory Comput. 2025 May 13;21(9):4792-4814. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.5c00319. Epub 2025 Apr 30. J Chem Theory Comput. 2025. PMID: 40307959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumgart T., Hess S.T., Webb W.W. Imaging coexisting fluid domains in biomembrane models coupling curvature and line tension. Nature. 2003;425:821–824. - PubMed
-
- Li Y., Ge M., Ciani L., Kuriakose G., Westover E.J., Dura M., Covey D.F., Freed J.H., Maxfield F.R., Lytton J., et al. Enrichment of endoplasmic reticulum with cholesterol inhibits sarcoplasmic-endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase-2b activity in parallel with increased order of membrane lipids: Implications for depletion of endoplasmic reticulum calcium stores and apoptosis in cholesterol-loaded macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:37030–37039. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

