Transcription of the SCL/TAL1 interrupting Locus (Stil) is required for cell proliferation in adult Zebrafish Retinas
- PMID: 24469449
- PMCID: PMC3945354
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.506295
Transcription of the SCL/TAL1 interrupting Locus (Stil) is required for cell proliferation in adult Zebrafish Retinas
Abstract
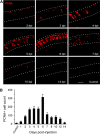
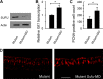
The human oncogene SCL/TAL1 interrupting locus (Stil) is highly conserved in vertebrate species. Previously, we identified a homolog of the Stil gene in zebrafish mutant (night blindness b, nbb), which showed neural defects in the retina (e.g. dopaminergic cell degeneration and/or lack of regeneration). In this research, we examined the roles of Stil in cell proliferation after degeneration in adult zebrafish retinas. We demonstrated that knockdown of Stil gene expression or inhibition of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling transduction decreases the rate of cell proliferation. In contrast, activation of Shh signal transduction promotes cell proliferation. In nbb(+/-) retinas, inhibition of SUFU (a repressor in the Shh pathway) rescues the defects in cell proliferation due to down-regulation of Stil gene expression. The latter data suggest that Stil play a role in cell proliferation through the Shh signal transduction pathway.
Keywords: Cell Proliferation; Neurons; Oncogene; Retina; Zebrafish.
Figures




References
-
- Aplan P. D., Lombardi D. P., Ginsberg A. M., Cossman J., Bertness V. L., Kirsch I. R. (1990) Disruption of the human scl locus by “illegitimate” v-(d)-j recombinase activity. Science 250, 1426–1429 - PubMed
-
- Collazo-Garcia N., Scherer P., Aplan P. (1995) Cloning and characterization of a murine SIL gene. Genomics 30, 506–513 - PubMed
-
- Izraeli S., Colaizzo-Anas T., Bertness V.L., Mani K., Aplan P. D., Kirsch I. R. (1997) Expression of the SIL gene is correlated with growth induction and cellular proliferation. Cell Growth Differ. 8, 1171–1179 - PubMed
-
- Izraeli S., Lowe L. A., Bertness V. L., Good D. J., Dorward D. W., Kirsch I. R., Kuehn M. R. (1999) The sil gene is required for mouse embryonic axial development and left-right specification. Nature 399, 691–694 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

