Isoform- and species-specific control of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptors by reactive oxygen species
- PMID: 24469450
- PMCID: PMC3961646
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.504159
Isoform- and species-specific control of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptors by reactive oxygen species
Abstract
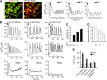
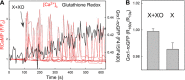
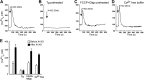
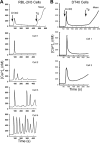
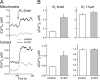
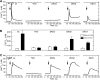
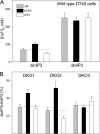
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) stimulate cytoplasmic [Ca(2+)] ([Ca(2+)]c) signaling, but the exact role of the IP3 receptors (IP3R) in this process remains unclear. IP3Rs serve as a potential target of ROS produced by both ER and mitochondrial enzymes, which might locally expose IP3Rs at the ER-mitochondrial associations. Also, IP3Rs contain multiple reactive thiols, common molecular targets of ROS. Therefore, we have examined the effect of superoxide anion (O2) on IP3R-mediated Ca(2+) signaling. In human HepG2, rat RBL-2H3, and chicken DT40 cells, we observed [Ca(2+)]c spikes and frequency-modulated oscillations evoked by a O2 donor, xanthine (X) + xanthine oxidase (XO), dose-dependently. The [Ca(2+)]c signal was mediated by ER Ca(2+) mobilization. X+XO added to permeabilized cells promoted the [Ca(2+)]c rise evoked by submaximal doses of IP3, indicating that O2 directly sensitizes IP3R-mediated Ca(2+) release. In response to X+XO, DT40 cells lacking two of three IP3R isoforms (DKO) expressing either type 1 (DKO1) or type 2 IP3Rs (DKO2) showed a [Ca(2+)]c signal, whereas DKO expressing type 3 IP3R (DKO3) did not. By contrast, IgM that stimulates IP3 formation, elicited a [Ca(2+)]c signal in every DKO. X+XO also facilitated the Ca(2+) release evoked by submaximal IP3 in permeabilized DKO1 and DKO2 but was ineffective in DKO3 or in DT40 lacking every IP3R (TKO). However, X+XO could also facilitate the effect of suboptimal IP3 in TKO transfected with rat IP3R3. Although in silico studies failed to identify a thiol missing in the chicken IP3R3, an X+XO-induced redox change was documented only in the rat IP3R3. Thus, ROS seem to specifically sensitize IP3Rs through a thiol group(s) within the IP3R, which is probably inaccessible in the chicken IP3R3.
Keywords: Calcium Signaling; Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER); IP3 Receptor; Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate; Mitochondria; Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS).
Figures



References
-
- Berridge M. J. (2009) Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1793, 933–940 - PubMed
-
- Mikoshiba K. (2007) IP3 receptor/Ca2+ channel: from discovery to new signaling concepts. J. Neurochem. 102, 1426–1446 - PubMed
-
- Petersen O. H., Tepikin A. V. (2008) Polarized calcium signaling in exocrine gland cells. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 70, 273–299 - PubMed
-
- Sanderson M. J., Delmotte P., Bai Y., Perez-Zogbhi J. F. (2008) Regulation of airway smooth muscle cell contractility by Ca2+ signaling and sensitivity. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 5, 23–31 - PubMed
-
- Lewis R. S. (2001) Calcium signaling mechanisms in T lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 497–521 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

