On the dephasing of genetic oscillators
- PMID: 24469814
- PMCID: PMC3926054
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1323433111
On the dephasing of genetic oscillators
Abstract
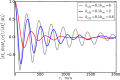
The digital nature of genes combined with the associated low copy numbers of proteins regulating them is a significant source of stochasticity, which affects the phase of biochemical oscillations. We show that unlike ordinary chemical oscillators, the dichotomic molecular noise of gene state switching in gene oscillators affects the stochastic dephasing in a way that may not always be captured by phenomenological limit cycle-based models. Through simulations of a realistic model of the NFκB/IκB network, we also illustrate the dephasing phenomena that are important for reconciling single-cell and population-based experiments on gene oscillators.
Keywords: gene networks; master equation; stochastic simulations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


 , and the ratio of oscillation frequency
, and the ratio of oscillation frequency  to decay rate γ. Different points correspond to different eigenvalues. Slow modes are grouped around
to decay rate γ. Different points correspond to different eigenvalues. Slow modes are grouped around  . Dominant rotational modes have a high
. Dominant rotational modes have a high  ratio.
ratio.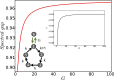

Similar articles
-
Efficient analysis of stochastic gene dynamics in the non-adiabatic regime using piecewise deterministic Markov processes.J R Soc Interface. 2018 Jan;15(138):20170804. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2017.0804. J R Soc Interface. 2018. PMID: 29386401 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic switching of delayed feedback suppresses oscillations in genetic regulatory systems.J R Soc Interface. 2023 Jun;20(203):20230059. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2023.0059. Epub 2023 Jun 28. J R Soc Interface. 2023. PMID: 37376870 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic modeling and numerical simulation of gene regulatory networks with protein bursting.J Theor Biol. 2017 May 21;421:51-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2017.03.017. Epub 2017 Mar 21. J Theor Biol. 2017. PMID: 28341132
-
Stochastic approaches in systems biology.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010 Jul-Aug;2(4):385-397. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.78. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20836037 Review.
-
Stochastic models for circadian rhythms: effect of molecular noise on periodic and chaotic behaviour.C R Biol. 2003 Feb;326(2):189-203. doi: 10.1016/s1631-0691(03)00016-7. C R Biol. 2003. PMID: 12754937 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular stripping, targets and decoys as modulators of oscillations in the NF-κB/IκBα/DNA genetic network.J R Soc Interface. 2016 Sep;13(122):20160606. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2016.0606. Epub 2016 Sep 28. J R Soc Interface. 2016. PMID: 27683001 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical clocks face a trade-off between internal and external noise resistance.Elife. 2018 Jul 10;7:e37624. doi: 10.7554/eLife.37624. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29988019 Free PMC article.
-
The Synergy of Thermal and Non-Thermal Effects in Hyperthermic Oncology.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 21;16(23):3908. doi: 10.3390/cancers16233908. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of DNA binding sites and slow unbinding kinetics in titration-based oscillators.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2015 Dec;92(6):062712. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.92.062712. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2015. PMID: 26764732 Free PMC article.
-
Protein sequestration versus Hill-type repression in circadian clock models.IET Syst Biol. 2016 Aug;10(4):125-35. doi: 10.1049/iet-syb.2015.0090. IET Syst Biol. 2016. PMID: 27444022 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Winfree A. The Geometry of Biological Time. New York: Springer; 2001.
-
- Morelli LG, Jülicher F. Precision of genetic oscillators and clocks. Phys Rev Lett. 2007;98(22):228101. - PubMed
-
- Goldbeter A. Biochemical Oscillations and Cellular Rhythms. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ Press; 1997.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

