A vertebrate myosin-I structure reveals unique insights into myosin mechanochemical tuning
- PMID: 24469830
- PMCID: PMC3926069
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1321022111
A vertebrate myosin-I structure reveals unique insights into myosin mechanochemical tuning
Abstract
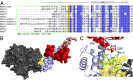
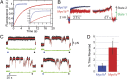
Myosins are molecular motors that power diverse cellular processes, such as rapid organelle transport, muscle contraction, and tension-sensitive anchoring. The structural adaptations in the motor that allow for this functional diversity are not known, due, in part, to the lack of high-resolution structures of highly tension-sensitive myosins. We determined a 2.3-Å resolution structure of apo-myosin-Ib (Myo1b), which is the most tension-sensitive myosin characterized. We identified a striking unique orientation of structural elements that position the motor's lever arm. This orientation results in a cavity between the motor and lever arm that holds a 10-residue stretch of N-terminal amino acids, a region that is divergent among myosins. Single-molecule and biochemical analyses show that the N terminus plays an important role in stabilizing the post power-stroke conformation of Myo1b and in tuning the rate of the force-sensitive transition. We propose that this region plays a general role in tuning the mechanochemical properties of myosins.
Keywords: cryo-EM; mechanochemistry; optical tweezers; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
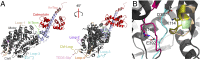

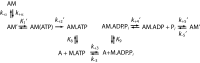
References
-
- De La Cruz EM, Ostap EM. Relating biochemistry and function in the myosin superfamily. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16(1):61–67. - PubMed
-
- Veigel C, Schmitz S, Wang F, Sellers JR. Load-dependent kinetics of myosin-V can explain its high processivity. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7(9):861–869. - PubMed
-
- Capitanio M, et al. Ultrafast force-clamp spectroscopy of single molecules reveals load dependence of myosin working stroke. Nat Methods. 2012;9(10):1013–1019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

