Deletion of Krüppel-like factor 4 in endothelial and hematopoietic cells enhances neointimal formation following vascular injury
- PMID: 24470523
- PMCID: PMC3959705
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000622
Deletion of Krüppel-like factor 4 in endothelial and hematopoietic cells enhances neointimal formation following vascular injury
Abstract
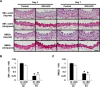
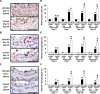
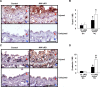
Background: Krüppel-like factor 4 (Klf4) is involved in a variety of cellular functions by activating or repressing the transcription of multiple genes. Results of previous studies showed that tamoxifen-inducible global deletion of the Klf4 gene in mice accelerated neointimal formation following vascular injury, in part via enhanced proliferation of smooth muscle cells (SMCs). Because Klf4 is also expressed in non-SMCs including endothelial cells (ECs), we determined if Tie2 promoter-dependent deletion of Klf4 in ECs and hematopoietic cells affected injury-induced neointimal formation.
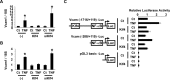
Methods and results: Klf4 conditional knockout (cKO) mice were generated by breeding Tie2-Cre mice and Klf4 floxed mice, and their phenotype was analyzed after carotid ligation injury. Results showed that injury-induced repression of SMC differentiation markers was unaffected by Tie2 promoter-dependent Klf4 deletion. However, of interest, neointimal formation was significantly enhanced in Klf4-cKO mice 21 days following carotid injury. Moreover, Klf4-cKO mice exhibited an augmented proliferation rate, enhanced accumulation of macrophages and T lymphocytes, and elevated expression of cell adhesion molecules including vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (Vcam1) and E-selectin in injured arteries. Mechanistic analyses in cultured ECs revealed that Klf4 inhibited tumor necrosis factor-α-induced expression of Vcam1 through blocking the binding of nuclear factor-κB to the Vcam1 promoter.
Conclusions: These results provide evidence that Klf4 in non-SMCs such as ECs regulates neointimal formation by repressing arterial inflammation following vascular injury.
Keywords: cell adhesion molecules; endothelium; krüppel‐like factors; smooth muscle; vascular injury.
Figures



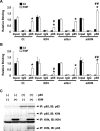
Comment in
-
Endothelial KLF4: crippling vascular injury?J Am Heart Assoc. 2014 Feb 26;3(1):e000769. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000769. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014. PMID: 24572258 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Selective Deletion of Leptin Signaling in Endothelial Cells Enhances Neointima Formation and Phenocopies the Vascular Effects of Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Sep;37(9):1683-1697. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309798. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28705795
-
Conditional deletion of Krüppel-like factor 4 delays downregulation of smooth muscle cell differentiation markers but accelerates neointimal formation following vascular injury.Circ Res. 2008 Jun 20;102(12):1548-57. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.176974. Epub 2008 May 15. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18483411 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupling Protein 2 Inhibits Myointimal Hyperplasia in Preclinical Animal Models of Vascular Injury.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Oct 12;6(10):e002641. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006593. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 29025747 Free PMC article.
-
The role of extracellular vesicles in neointima formation post vascular injury.Cell Signal. 2020 Dec;76:109783. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109783. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32956789 Review.
-
Role of Kruppel-like factor 4 in atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2021 Jan;512:135-141. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Clin Chim Acta. 2021. PMID: 33181148 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Atherosclerotic Potential of Free Fatty Acid Receptor 4 (FFAR4).Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 24;9(5):467. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050467. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33923318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shear Stress Regulation of Endothelium: A Double-edged Sword.J Transl Int Med. 2018 Jun 26;6(2):58-61. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2018-0019. eCollection 2018 Jun. J Transl Int Med. 2018. PMID: 29984197 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Participation of Krüppel-like Factors in Atherogenesis.Metabolites. 2023 Mar 19;13(3):448. doi: 10.3390/metabo13030448. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36984888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperhomocysteinemia induces vascular calcification by activating the transcription factor RUNX2 via Krüppel-like factor 4 up-regulation in mice.J Biol Chem. 2019 Dec 20;294(51):19465-19474. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009758. Epub 2019 Oct 18. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31628194 Free PMC article.
-
A paradigm of endothelium-protective and stent-free anti-restenotic therapy using biomimetic nanoclusters.Biomaterials. 2018 Sep;178:293-301. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.06.025. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Biomaterials. 2018. PMID: 29958152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002; 420:868-874 - PubMed
-
- Segre JA, Bauer C, Fuchs E. Klf4 is a transcription factor required for establishing the barrier function of the skin. Nat Genet. 1999; 22:356-360 - PubMed
-
- Katz JP, Perreault N, Goldstein BG, Actman L, McNally SR, Silberg DG, Furth EE, Kaestner KH. Loss of Klf4 in mice causes altered proliferation and differentiation and precancerous changes in the adult stomach. Gastroenterology. 2005; 128:935-945 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

