Human demodex mite: the versatile mite of dermatological importance
- PMID: 24470662
- PMCID: PMC3884930
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5154.123498
Human demodex mite: the versatile mite of dermatological importance
Abstract
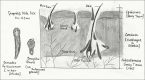
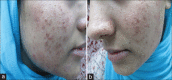
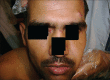
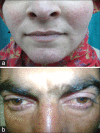
Demodex mite is an obligate human ecto-parasite found in or near the pilo-sebaceous units. Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis are two species typically found on humans. Demodex infestation usually remains asymptomatic and may have a pathogenic role only when present in high densities and also because of immune imbalance. All cutaneous diseases caused by Demodex mites are clubbed under the term demodicosis or demodicidosis, which can be an etiological factor of or resemble a variety of dermatoses. Therefore, a high index of clinical suspicion about the etiological role of Demodex in various dermatoses can help in early diagnosis and appropriate, timely, and cost effective management.
Keywords: Demodex; demodicidosis; demodicosis; ecto-parasite.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Norn MS. Demodex folliculorum. Incidence, regional distribution, pathogenicity. Dan Med Bull. 1971;18:14–7. - PubMed
-
- Rufli T, Mumcuoglu Y. The hair follicle mites Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis: Biology and medical importance. A review. Dermatologica. 1981;162:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Baima B, Sticherling M. Demodicidosis revisited. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002;82:3–6. - PubMed
-
- Aylesworth R, Vance C. Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis in cutaneous biopsies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;7:583–9. - PubMed
-
- Basta- Juzbasic A, Subic JS, Ljubojevic S. Demodex folliculorum in development of dermatitis rosaceiformis steroidica and rosacea-related diseases. Clin Dermatol. 2002;20:135–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
