Human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus: subtle differences but comparable severity
- PMID: 24470892
- PMCID: PMC3892583
- DOI: 10.4081/idr.2010.e12
Human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus: subtle differences but comparable severity
Abstract
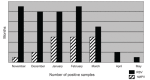
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a recently discovered virus that causes respiratory illness in children that can lead to hospitalization. Our study was undertaken to further understand hMPV-associated illness, compare clinical characteristics of hMPV and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and establish the utility of routine screening for hMPV. We retrospectively identified hMPV-associated illnesses described among children with respiratory symptoms admitted to a tertiary care center in southeast Michigan during the 2006-2007 respiratory viral season. A convenience sample of 256 nasopharyngeal specimens was subjected to nucleic acid extraction and amplification to identify those specimens positive for hMPV. A medical record review was undertaken to retrieve demographic and clinical data of patients with hMPV, comparing them to RSV-positive patients and patients evaluated for respiratory symptoms who were negative for hMPV and RSV. We found that hMPV was the second most commonly identified virus after RSV. hMPV-positive patients were older than RSV-positive patients. Among hMPV-positive patients, pneumonia was diagnosed in 37.5% and bronchiolitis in 31.2%, peribronchial cuffing was present on chest radiographs of 37.5%, antibiotic treatment was used in 81.2%, and admission to the ICU was seen in 37.5%. Finally, hMPV-positive patients were more likely to have fever than RSV-positive patients or patients negative for hMPV and RSV. We concluded that hMPV is a major pathogen associated with hospitalization of children and with the same severity of illness as RSV but in a slightly older population. Because of the apparent prevalence and severity of illness, routine screening should be implemented.
Keywords: human metapneumovirus; respiratory syncytial virus; severity..
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: the authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Boivin G, Abed Y, Pelletier G, et al. Virological features and clinical manifestations associated with human metapneumovirus: a new paramyxovirus responsible for acute respiratory-tract infections in all age groups. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:1330–4. - PubMed
-
- Esper F, Boucher D, Weibel C, et al. Human metapneumovirus infection in the United States: clinical manifestations associated with a newly emerging respiratory infection in children. Pediatrics. 2003;111:1407–10. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources