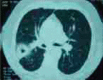
A cavitary pneumonia caused by leptotrichia species in an immunocompetent patient
- PMID: 24470931
- PMCID: PMC3892657
- DOI: 10.4081/idr.2012.e24
A cavitary pneumonia caused by leptotrichia species in an immunocompetent patient
Abstract
Leptotrichia species (LS) is an anaerobic Gram negative bacillus in the Bacteroidaceae family and part of the normal human oral flora. It is rarely pathogenic, but occasionally causes diseases in immunocompromised hosts. I am reporting a case of cavitary pneumonia caused by LS in an immunocompetent host.
Keywords: Leptotrichia sp; cavitary pneumonia; immunocompetent patient..
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leptotrichia species in human infections II.J Oral Microbiol. 2017 Sep 15;9(1):1368848. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2017.1368848. eCollection 2017. J Oral Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29081911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serious infection with Leptotrichia buccalis. Report of a case and review of the literature.Am J Med. 1980 Nov;69(5):782-5. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90452-0. Am J Med. 1980. PMID: 7001901 Review.
-
Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis with Leptotrichia goodfellowii in a Patient with a Valvular Allograft: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Case Rep Infect Dis. 2016;2016:3051212. doi: 10.1155/2016/3051212. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27895947 Free PMC article.
-
Leptotrichia goodfellowii Infection: Case Report and Literature Review.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016 Winter;46(1):83-6. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016. PMID: 26927348 Review.
-
Hepatic abscess likely related to Leptotrichia buccalis in an immunocompetent patient.Liver. 1996 Oct;16(5):342-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1996.tb00758.x. Liver. 1996. PMID: 8938638
Cited by
-
Increased Abundance of Achromobacter xylosoxidans and Bacillus cereus in Upper Airway Transcriptionally Active Microbiome of COVID-19 Mortality Patients Indicates Role of Co-Infections in Disease Severity and Outcome.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0231121. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02311-21. Epub 2022 May 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35579429 Free PMC article.
-
Leptotrichia species in human infections II.J Oral Microbiol. 2017 Sep 15;9(1):1368848. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2017.1368848. eCollection 2017. J Oral Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29081911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking the westernised oropharyngeal microbiome to the immune response in Chinese immigrants.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2020 Jul 25;16:67. doi: 10.1186/s13223-020-00465-7. eCollection 2020. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32944027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhally HS, Lema C, Romagnoli M, et al. Leptotrichia buccalis bacteremia in two patients with acute myelogenous leukemia. Anaerobe. 2005;11:350–3. - PubMed
-
- Weinberer M, Wu T, Rubin M, et al. Leptotrichia buccalis bacteremia in patients with cancer: report of four cases and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13:201–6. - PubMed
-
- Vemelen K, Mertens I, Thomas J, et al. Bacteremia with Leptotrichia buccalis: report of a case and review of the literature. Acta Clin Belg. 1996;51:265–70. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz DN, Schable B, Tenover FC, Miller RA. Leptotrichia buccalis bacteremia in patients treated in a single bone marrow transplant unit. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:762–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources