JAK2-STAT5B pathway and osteoblast differentiation
- PMID: 24470975
- PMCID: PMC3894232
- DOI: 10.4161/jkst.24931
JAK2-STAT5B pathway and osteoblast differentiation
Abstract
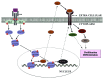
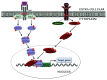
Osteoblast differentiation is a critical step in the maintenance of bone homeostasis. Osteoblast differentiation is generally maintained by growth hormone (GH) and various other endocrine and autocrine/paracrine factors. JAK2-STAT5B pathway is a central axis in the mechanism of GH signaling. Similarly, the autocrine/paracrine signaling factor IGF-1 also mediates its effects through this pathway. Analysis on JAK2-STAT5B pathway showed its importance in the IGF-1/IGF-1R mediated regulation of gene expression and osteoblast differentiation. Persistent activation of STAT5B and inhibition of STAT5B degradation showed increased osteoblastic differentiation and STAT5B/Runx-2 activities. Conditional gene silencing studies showed the importance of the JAK2-STAT5B pathway in stimulation of other transcription factors and expression of various differentiation markers.
Keywords: BMPs; IGF-1R; JAK2-STAT5B; growth hormone receptor; osteoblast differentiation.
Figures

References
-
- Noble B. Bone microdamage and cell apoptosis. Eur Cell Mater. 2003;6:46–55, 55. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
