Simplified 2-aminoquinoline-based scaffold for potent and selective neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition
- PMID: 24472039
- PMCID: PMC3954451
- DOI: 10.1021/jm401838x
Simplified 2-aminoquinoline-based scaffold for potent and selective neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition
Abstract
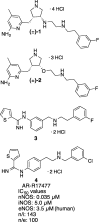
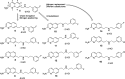
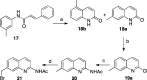
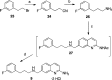
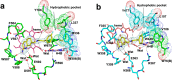
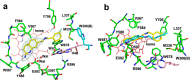
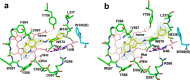
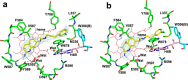
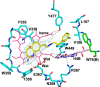
Since high levels of nitric oxide (NO) are implicated in neurodegenerative disorders, inhibition of the neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) and reduction of NO levels are therapeutically desirable. Nonetheless, many nNOS inhibitors mimic l-arginine and are poorly bioavailable. 2-Aminoquinoline-based scaffolds were designed with the hope that they could (a) mimic aminopyridines as potent, isoform-selective arginine isosteres and (b) possess chemical properties more conducive to oral bioavailability and CNS penetration. A series of these compounds was synthesized and assayed against purified nNOS enzymes, endothelial NOS (eNOS), and inducible NOS (iNOS). Several compounds built on a 7-substituted 2-aminoquinoline core are potent and isoform-selective; X-ray crystallography indicates that aminoquinolines exert inhibitory effects by mimicking substrate interactions with the conserved active site glutamate residue. The most potent and selective compounds, 7 and 15, were tested in a Caco-2 assay and showed good permeability and low efflux, suggesting high potential for oral bioavailability.
Figures

References
-
- Uehara T.; Nakamura T.; Yao D.; Shi Z. Q.; Gu Z.; Ma Y.; Masliah E.; Nomura Y.; Lipton S. A. S-Nitrosylated protein-disulphide isomerase links protein misfolding to neurodegeneration. Nature 2006, 441, 513–517. - PubMed
-
- Torreilles F.; Salman-Tabcheh S.; Guerin M.; Torreilles J. Neurodegenerative disorders: the role of peroxynitrite. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 30, 153–163. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L.; Dawson V. L.; Dawson T. M. Role of nitric oxide in Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 109, 33–41. - PubMed
-
- Dorheim M.-A.; Tracey W. R.; Pollock J. S.; Grammas P. Nitric oxide synthase activity is elevated in brain microvessels in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 205, 659–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

