Postmortem examination of patient H.M.'s brain based on histological sectioning and digital 3D reconstruction
- PMID: 24473151
- PMCID: PMC3916843
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4122
Postmortem examination of patient H.M.'s brain based on histological sectioning and digital 3D reconstruction
Abstract
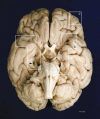
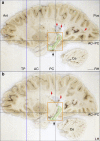
Modern scientific knowledge of how memory functions are organized in the human brain originated from the case of Henry G. Molaison (H.M.), an epileptic patient whose amnesia ensued unexpectedly following a bilateral surgical ablation of medial temporal lobe structures, including the hippocampus. The neuroanatomical extent of the 1953 operation could not be assessed definitively during H.M.'s life. Here we describe the results of a procedure designed to reconstruct a microscopic anatomical model of the whole brain and conduct detailed 3D measurements in the medial temporal lobe region. This approach, combined with cellular-level imaging of stained histological slices, demonstrates a significant amount of residual hippocampal tissue with distinctive cytoarchitecture. Our study also reveals diffuse pathology in the deep white matter and a small, circumscribed lesion in the left orbitofrontal cortex. The findings constitute new evidence that may help elucidate the consequences of H.M.'s operation in the context of the brain's overall pathology.
Figures





References
-
- Corkin S. Lasting consequences of bilateral medial temporal lobectomy: clinical course and experimental findings in H.M. Sem. Neurol. 4, 249–259 (1984).
-
- Corkin S. Tactually-guided maze learning in man: Effects of unilateral cortical excisions and bilateral hippocampal lesions. Neuropsychologia 3, 339–351 (1965).
-
- Corkin S. Acquisition of motor skill after bilateral medial temporal-lobe excision. Neuropsychologia 6, 255–265 (1968).
-
- Woodruff-Pak D. S. Delay and trace paradigms. Behav. Neurosci. 107, 911–925 (1993). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

