Long-term effects of a Palaeolithic-type diet in obese postmenopausal women: a 2-year randomized trial
- PMID: 24473459
- PMCID: PMC4216932
- DOI: 10.1038/ejcn.2013.290
Long-term effects of a Palaeolithic-type diet in obese postmenopausal women: a 2-year randomized trial
Abstract
Background/objectives: Short-term studies have suggested beneficial effects of a Palaeolithic-type diet (PD) on body weight and metabolic balance. We now report the long-term effects of a PD on anthropometric measurements and metabolic balance in obese postmenopausal women, in comparison with a diet according to the Nordic Nutrition Recommendations (NNR).
Subjects/methods: Seventy obese postmenopausal women (mean age 60 years, body mass index 33 kg/m(2)) were assigned to an ad libitum PD or NNR diet in a 2-year randomized controlled trial. The primary outcome was change in fat mass as measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry.
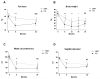
Results: Both groups significantly decreased total fat mass at 6 months (-6.5 and-2.6 kg) and 24 months (-4.6 and-2.9 kg), with a more pronounced fat loss in the PD group at 6 months (P<0.001) but not at 24 months (P=0.095). Waist circumference and sagittal diameter also decreased in both the groups, with a more pronounced decrease in the PD group at 6 months (-11.1 vs-5.8 cm, P=0.001 and-3.7 vs-2.0 cm, P<0.001, respectively). Triglyceride levels decreased significantly more at 6 and 24 months in the PD group than in the NNR group (P<0.001 and P=0.004). Nitrogen excretion did not differ between the groups.
Conclusions: A PD has greater beneficial effects vs an NNR diet regarding fat mass, abdominal obesity and triglyceride levels in obese postmenopausal women; effects not sustained for anthropometric measurements at 24 months. Adherence to protein intake was poor in the PD group. The long-term consequences of these changes remain to be studied.
Figures

References
-
- Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, et al. National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet. 2011;377:557–567. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2224–2260. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rexrode KM, Carey VJ, Hennekens CH, Walters EE, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, et al. Abdominal adiposity and coronary heart disease in women. JAMA. 1998;280:1843–1848. - PubMed
-
- Davis SR, Castelo-Branco C, Chedraui P, Lumsden MA, Nappi RE, Shah D, et al. Understanding weight gain at menopause. Climacteric. 2012;15:419–429. - PubMed
-
- Te Morenga L, Mann J. The role of high-protein diets in body weight management and health. Br J Nutr. 2012;108(Suppl 2):S130–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

