Mendelian randomization of blood lipids for coronary heart disease
- PMID: 24474739
- PMCID: PMC4344957
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht571
Mendelian randomization of blood lipids for coronary heart disease
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the causal role of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and triglycerides in coronary heart disease (CHD) using multiple instrumental variables for Mendelian randomization.
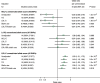
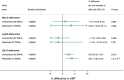
Methods and results: We developed weighted allele scores based on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with established associations with HDL-C, triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). For each trait, we constructed two scores. The first was unrestricted, including all independent SNPs associated with the lipid trait identified from a prior meta-analysis (threshold P < 2 × 10(-6)); and the second a restricted score, filtered to remove any SNPs also associated with either of the other two lipid traits at P ≤ 0.01. Mendelian randomization meta-analyses were conducted in 17 studies including 62,199 participants and 12,099 CHD events. Both the unrestricted and restricted allele scores for LDL-C (42 and 19 SNPs, respectively) associated with CHD. For HDL-C, the unrestricted allele score (48 SNPs) was associated with CHD (OR: 0.53; 95% CI: 0.40, 0.70), per 1 mmol/L higher HDL-C, but neither the restricted allele score (19 SNPs; OR: 0.91; 95% CI: 0.42, 1.98) nor the unrestricted HDL-C allele score adjusted for triglycerides, LDL-C, or statin use (OR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.44, 1.46) showed a robust association. For triglycerides, the unrestricted allele score (67 SNPs) and the restricted allele score (27 SNPs) were both associated with CHD (OR: 1.62; 95% CI: 1.24, 2.11 and 1.61; 95% CI: 1.00, 2.59, respectively) per 1-log unit increment. However, the unrestricted triglyceride score adjusted for HDL-C, LDL-C, and statin use gave an OR for CHD of 1.01 (95% CI: 0.59, 1.75).
Conclusion: The genetic findings support a causal effect of triglycerides on CHD risk, but a causal role for HDL-C, though possible, remains less certain.
Keywords: Aetiology; Epidemiology; Heart disease; Lipids; Mendelian randomization.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


References
-
- Mihaylova B, Emberson J, Blackwell L, Keech A, Simes J, Barnes EH, Voysey M, Gray A, Collins R, Baigent C. The effects of lowering LDL cholesterol with statin therapy in people at low risk of vascular disease: meta-analysis of individual data from 27 randomised trials. Lancet. 2012;380:581–590. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baigent C, Keech A, Kearney PM, Blackwell L, Buck G, Pollicino C, Kirby A, Sourjina T, Peto R, Collins R, Simes R. Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet. 2005;366:1267–1278. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz GG, Olsson AG, Abt M, Ballantyne CM, Barter PJ, Brumm J, Chaitman BR, Holme IM, Kallend D, Leiter LA, Leitersdorf E, McMurray JJ, Mundl H, Nicholls SJ, Shah PK, Tardif JC, Wright RS. Effects of dalcetrapib in patients with a recent acute coronary syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:2089–2099. - PubMed
-
- Keech A, Simes RJ, Barter P, Best J, Scott R, Taskinen MR, Forder P, Pillai A, Davis T, Glasziou P, Drury P, Kesaniemi YA, Sullivan D, Hunt D, Colman P, d'Emden M, Whiting M, Ehnholm C, Laakso M investigators Fs. Effects of long-term fenofibrate therapy on cardiovascular events in 9795 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the FIELD study): randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;366:1849–1861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200960009C/PHS HHS/United States
- N01 HC055020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55019/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL36310/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CZB/4/672/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- N01 HC055016/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/13/2/30098/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RG/08/008/25291/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 33014/PHS HHS/United States
- PG/13/66/30442/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01WH42129-32/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055019/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL036310/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K006215/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-55022/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RR-024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55016/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32100-2/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH022110/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/07/131/24254/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- CH/98001/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12019/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32108-9/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55021/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42107-26/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55015/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32122/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-55020/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG 08/008/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01AG1764406S1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RG/07/005/23633/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01WH32105-6/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32111-13/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32118-32119/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/Z/09/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AG017644/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K006584/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K013351/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055022/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0802432/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/13/16/30528/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-55018/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065226/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G1000718/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01WH32115/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01629X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01WH44221/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/07/133/24260/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/8/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-65226/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/10/12/28456/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01WH24152/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

