Integrated description of protein dynamics from room-temperature X-ray crystallography and NMR
- PMID: 24474795
- PMCID: PMC3910589
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1323440111
Integrated description of protein dynamics from room-temperature X-ray crystallography and NMR
Abstract
Detailed descriptions of atomic coordinates and motions are required for an understanding of protein dynamics and their relation to molecular recognition, catalytic function, and allostery. Historically, NMR relaxation measurements have played a dominant role in the determination of the amplitudes and timescales (picosecond-nanosecond) of bond vector fluctuations, whereas high-resolution X-ray diffraction experiments can reveal the presence of and provide atomic coordinates for multiple, weakly populated substates in the protein conformational ensemble. Here we report a hybrid NMR and X-ray crystallography analysis that provides a more complete dynamic picture and a more quantitative description of the timescale and amplitude of fluctuations in atomic coordinates than is obtainable from the individual methods alone. Order parameters (S(2)) were calculated from single-conformer and multiconformer models fitted to room temperature and cryogenic X-ray diffraction data for dihydrofolate reductase. Backbone and side-chain order parameters derived from NMR relaxation experiments are in excellent agreement with those calculated from the room-temperature single-conformer and multiconformer models, showing that the picosecond timescale motions observed in solution occur also in the crystalline state. These motions are quenched in the crystal at cryogenic temperatures. The combination of NMR and X-ray crystallography in iterative refinement promises to provide an atomic resolution description of the alternate conformational substates that are sampled through picosecond to nanosecond timescale fluctuations of the protein structure. The method also provides insights into the structural heterogeneity of nonmethyl side chains, aromatic residues, and ligands, which are less commonly analyzed by NMR relaxation measurements.
Keywords: B factor; Lipari-Szabo; atomic displacement parameters; nuclear magnetic resonance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
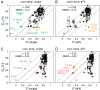
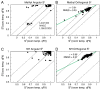
 for methyl groups with values calculated from a single structure (A) and a multistate qFit model (B) at room temperature. Residues in green improve their fit to the experimental data in the qFit model, whereas residues in orange appear as outliers in both single and qFit models. Dashed lines indicate ±0.2 from ideal agreement. For comparison, C and D show order parameters for a crystal at cryogenic temperature, single and multistate qFit models, respectively. Residues in blue improve agreement in the qFit model, whereas residues in red appear to have the same order parameters at both temperatures.
for methyl groups with values calculated from a single structure (A) and a multistate qFit model (B) at room temperature. Residues in green improve their fit to the experimental data in the qFit model, whereas residues in orange appear as outliers in both single and qFit models. Dashed lines indicate ±0.2 from ideal agreement. For comparison, C and D show order parameters for a crystal at cryogenic temperature, single and multistate qFit models, respectively. Residues in blue improve agreement in the qFit model, whereas residues in red appear to have the same order parameters at both temperatures.
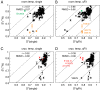
 and
and  components of the order parameters for the methyl (A and B) and NH (C and D) order parameters. The line of best fit for the temperature dependence of
components of the order parameters for the methyl (A and B) and NH (C and D) order parameters. The line of best fit for the temperature dependence of  (green) is shown in B and D.
(green) is shown in B and D.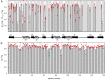
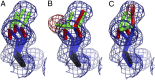
References
-
- Lange OF, et al. Recognition dynamics up to microseconds revealed from an RDC-derived ubiquitin ensemble in solution. Science. 2008;320(5882):1471–1475. - PubMed
-
- Boehr DD, McElheny D, Dyson HJ, Wright PE. The dynamic energy landscape of dihydrofolate reductase catalysis. Science. 2006;313(5793):1638–1642. - PubMed
-
- Eisenmesser EZ, et al. Intrinsic dynamics of an enzyme underlies catalysis. Nature. 2005;438(7064):117–121. - PubMed
-
- Gunasekaran K, Ma B, Nussinov R. Is allostery an intrinsic property of all dynamic proteins? Proteins. 2004;57(3):433–443. - PubMed
-
- Shaanan B, et al. Combining experimental information from crystal and solution studies: Joint X-ray and NMR refinement. Science. 1992;257(5072):961–964. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions

