Stillbirth during infection with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
- PMID: 24474813
- PMCID: PMC4618552
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiu068
Stillbirth during infection with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
Abstract
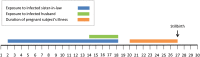
We conducted an epidemiologic investigation among survivors of an outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection in Jordan. A second-trimester stillbirth occurred during the course of an acute respiratory illness that was attributed to MERS-CoV on the basis of exposure history and positive results of MERS-CoV serologic testing. This is the first occurrence of stillbirth during an infection with MERS-CoV and may have bearing upon the surveillance and management of pregnant women in settings of unexplained respiratory illness potentially due to MERS-CoV. Future prospective investigations of MERS-CoV should ascertain pregnancy status and obtain further pregnancy-related data, including biological specimens for confirmatory testing.
Keywords: EMC-CoV; Jordan; MERS-CoV; Middle East respiratory syndrome; birth outcomes; novel coronavirus; pneumonia; pregnancy; severe acute respiratory illness; stillbirth.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2014. This work is written by (a) US Government employee(s) and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures
References
-
- Hijawi B, Abdallat M, Sayaydeh A, et al. Novel coronavirus infections in Jordan, April 2012: epidemiological findings from a retrospective investigation. East Med H J. 2013;19:S12–8. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global Alert and Response. Revised interim case definition for reporting to WHO—Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) http://www.who.int/csr/disease/coronavirus_infections/case_definition/en/ . Accessed 28 August 2013.
-
- Jamieson DJ, Honein MA, Rasmussen SA, et al. H1N1 2009 influenza virus infection during pregnancy in the USA. Lancet. 2009;374:451–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical