Caveolin-1 provides palliation for adverse hepatic reactions in hypercholesterolemic rabbits
- PMID: 24475013
- PMCID: PMC3901645
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071862
Caveolin-1 provides palliation for adverse hepatic reactions in hypercholesterolemic rabbits
Abstract
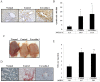
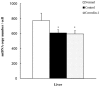
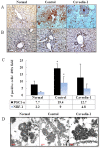
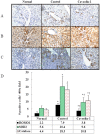
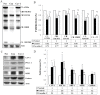
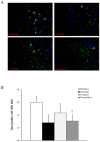
Caveolins are an essential component of cholesterol-rich invaginations of the plasma membrane known as caveolae. These flask-shaped, invaginated structures participate in a number of important cellular processes, including vesicular transport, cholesterol homeostasis, and signal transduction. We investigated the effects of CAV-1 on mitochondrial biogenesis and antioxidant enzymes in hypercholesterolemia-affected target organs. A total of eighteen male New Zealand white rabbits were divided into three groups: a normal-diet group, an untreated hypercholesterolemia-induced group, and a hypercholesterolemia-induced group that received intravenous administration of antennapedia-CAV-1 (AP-CAV-1) peptide every 2 days for 2 weeks. Serum biochemistry, CAV-1 distribution, neutral lipid distribution, mitochondrial morphology, biogenesis-mediated protein content, oxidative stress balance, antioxidant enzyme levels, and apoptotic cell death of liver tissue were analysed. Hepatic and circulating cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels differed significantly between the three groups (P<0.05). Immunohistochemical staining intensity of CAV-1 was greater in AP-CAV-1-treated rabbits than in untreated rabbits, especially in the vicinity of the liver vasculature. The high levels of neutral lipids, malondialdehyde, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactive 1α (PGC-1α), and nuclear respiratory factor-1 (NRF-1) seen in untreated hypercholesteremic animals were attenuated by administration of AP-CAV-1 (P<0.05). In addition, mitochondria in animals that received treatment exhibited darker electron-dense matrix and integrated cristae. Furthermore, the levels of ROS modulator 1 (Romo1) and superoxide dismutase (SOD)-2, as well as catalase activity were significantly lower in CAV-1-treated hypercholesterolemic rabbits (P<0.05). AP-CAV-1 treatment also restored mitochondrial respiratory chain subunit protein content (OXPHOS complexes I-V), thereby preserving mitochondrial function (P<0.05). Furthermore, AP-CAV-1 treatment significantly suppressed apoptotic cell death, as evidenced by a reduction in the number of TUNEL-positive cells. Our results indirectly indicate that CAV-1 mediates the negative effects of PGC-1α on hepatic mitochondrial respiratory chain function, promotes the antioxidant enzyme defence system, and maintains mitochondrial biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caveolin-1 Expression Ameliorates Nephrotic Damage in a Rabbit Model of Cholesterol-Induced Hypercholesterolemia.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 28;11(4):e0154210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154210. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27124120 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) producing Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) alleviates age associated oxidative stress and hyperlipidemia, and improves mitochondrial function in ageing rats.Exp Gerontol. 2015 Jun;66:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Exp Gerontol. 2015. PMID: 25843018
-
Effects of flaxseed oil on serum lipids and atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic rabbits.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Sep;8(3):227-35. doi: 10.1177/107424840300800308. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2003. PMID: 14506548
-
[Caveolin-1: oxidative stress target in tumor cells].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2019 Oct 25;71(5):792-798. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31646333 Review. Chinese.
-
Tumor microenvironment and metabolic synergy in breast cancers: critical importance of mitochondrial fuels and function.Semin Oncol. 2014 Apr;41(2):195-216. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2014.03.002. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Semin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24787293 Review.
Cited by
-
Caveolae and lipid sorting: Shaping the cellular response to stress.J Cell Biol. 2020 Apr 6;219(4):e201905071. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201905071. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32328645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise-Induced Changes in Caveolin-1, Depletion of Mitochondrial Cholesterol, and the Inhibition of Mitochondrial Swelling in Rat Skeletal Muscle but Not in the Liver.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:3620929. doi: 10.1155/2016/3620929. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 26839631 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of siRNA delivery enhancers by a chemical library screen.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Sep 18;43(16):7984-8001. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv762. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26220182 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 in the regulation of cell metabolism: a cancer perspective.Mol Cancer. 2016 Nov 16;15(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0558-7. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27852311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic caveolin-1 is enhanced in Cyp27a1/ApoE double knockout mice.FEBS Open Bio. 2016 Sep 26;6(10):1025-1035. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12123. eCollection 2016 Oct. FEBS Open Bio. 2016. PMID: 28149711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jasmin JF, Frank PG, Lisanti MP (2012) Caveolins and Caveolae: Roles in Signaling and Disease Mechanisms. Adv Exp Med Biol 729 section II: 145–156. - PubMed
-
- Pavlides S, Gutierrez-Pajares JL, Danilo C, Lisanti MP, Frank PG (2012) Atherosclerosis caveolae and caveolin-1. Adv Exp Med Biol 729: 127–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

