RNA control of HIV-1 particle size polydispersity
- PMID: 24475027
- PMCID: PMC3901647
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083874
RNA control of HIV-1 particle size polydispersity
Abstract
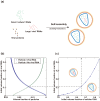
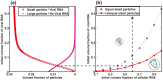
HIV-1, an enveloped RNA virus, produces viral particles that are known to be much more heterogeneous in size than is typical of non-enveloped viruses. We present here a novel strategy to study HIV-1 Viral Like Particles (VLP) assembly by measuring the size distribution of these purified VLPs and subsequent viral cores thanks to Atomic Force Microscopy imaging and statistical analysis. This strategy allowed us to identify whether the presence of viral RNA acts as a modulator for VLPs and cores size heterogeneity in a large population of particles. These results are analyzed in the light of a recently proposed statistical physics model for the self-assembly process. In particular, our results reveal that the modulation of size distribution by the presence of viral RNA is qualitatively reproduced, suggesting therefore an entropic origin for the modulation of RNA uptake by the nascent VLP.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
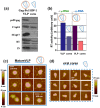
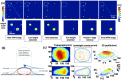
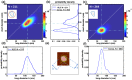
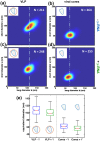
References
-
- Bancroft JB, Hiebert E (1967) Formation of an infectious nucleoprotein from protein and nucleic acid isolated from a small spherical virus. Virology 32: 354–356. - PubMed
-
- Lavelle L, Gingery M, Phillips M, Gelbart WM, Knobler CM, et al. (2009) Phase diagram of self-assembled viral capsid protein polymorphs. J Phys Chem B 113: 3813–3819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

