Mining gene expression data for pollutants (dioxin, toluene, formaldehyde) and low dose of gamma-irradiation
- PMID: 24475070
- PMCID: PMC3901678
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086051
Mining gene expression data for pollutants (dioxin, toluene, formaldehyde) and low dose of gamma-irradiation
Abstract
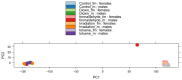
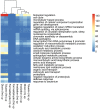
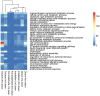
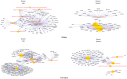
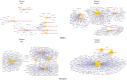
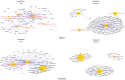
General and specific effects of molecular genetic responses to adverse environmental factors are not well understood. This study examines genome-wide gene expression profiles of Drosophila melanogaster in response to ionizing radiation, formaldehyde, toluene, and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. We performed RNA-seq analysis on 25,415 transcripts to measure the change in gene expression in males and females separately. An analysis of the genes unique to each treatment yielded a list of genes as a gene expression signature. In the case of radiation exposure, both sexes exhibited a reproducible increase in their expression of the transcription factors sugarbabe and tramtrack. The influence of dioxin up-regulated metabolic genes, such as anachronism, CG16727, and several genes with unknown function. Toluene activated a gene involved in the response to the toxins, Cyp12d1-p; the transcription factor Fer3's gene; the metabolic genes CG2065, CG30427, and CG34447; and the genes Spn28Da and Spn3, which are responsible for reproduction and immunity. All significantly differentially expressed genes, including those shared among the stressors, can be divided into gene groups using Gene Ontology Biological Process identifiers. These gene groups are related to defense response, biological regulation, the cell cycle, metabolic process, and circadian rhythms. KEGG molecular pathway analysis revealed alteration of the Notch signaling pathway, TGF-beta signaling pathway, proteasome, basal transcription factors, nucleotide excision repair, Jak-STAT signaling pathway, circadian rhythm, Hippo signaling pathway, mTOR signaling pathway, ribosome, mismatch repair, RNA polymerase, mRNA surveillance pathway, Hedgehog signaling pathway, and DNA replication genes. Females and, to a lesser extent, males actively metabolize xenobiotics by the action of cytochrome P450 when under the influence of dioxin and toluene. Finally, in this work we obtained gene expression signatures pollutants (dioxin, toluene), low dose of gamma-irradiation and common molecular pathways for different kind of stressors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- UNSCEAR (2010) Report of the United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation: “Summary of low-dose radiation effects on health”. UNITED NATIONS. pp. 106.
-
- Kim KH, Jahan SA, Lee JT (2011) Exposure to formaldehyde and its potential human health hazards. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 29: 277–299. - PubMed
-
- IARC (1997) Polychlorinated Dibenzo-Para-Dioxins and Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans. LyonFrance: World Health Organization. 666 p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

