Efficacy and safety of talc pleurodesis for malignant pleural effusion: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 24475222
- PMCID: PMC3903610
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087060
Efficacy and safety of talc pleurodesis for malignant pleural effusion: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Talc pleurodesis has been widely used to control malignant pleural effusion; however, it is still not clear whether talc pleurodesis is more effective than other local therapies. We performed a meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy and safety of talc pleurodesis in the management of malignant pleural effusion.
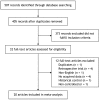
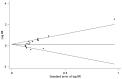
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science were searched for English-language studies of clinical controlled trials comparing talc pleurodesis with control therapies until August 8, 2013. Success rate and incidence of adverse events were evaluated. Relative risks were estimated using random- or fixed- effects model and statistical heterogeneity was assessed using I² test.
Results: Twenty trials involving 1,525 patients with malignant pleural effusion were included. The success rate of talc pleurodesis was significantly higher than that of control therapies (relative risk, 1.21; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.45; p = 0.035) with similar adverse events. In addition, thoracoscopic talc poudrage was more effective than bedside talc slurry (relative risk, 1.12; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.23; p = 0.026).
Conclusions: The current evidences suggested the benefit for talc pleurodesis in the treatment of malignant pleural effusion. Talc pleurodesis, especially thoracoscopic talc poudrage pleurodesis, should be performed in patients with malignant pleural effusion, especially those with life-expectancy longer than one month.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thoracoscopy and talc poudrage compared with intercostal drainage and talc slurry infusion to manage malignant pleural effusion: the TAPPS RCT.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Jun;24(26):1-90. doi: 10.3310/hta24260. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32525474 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Talc poudrage versus talc slurry in the treatment of malignant pleural effusion. A prospective comparative study.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006 Dec;30(6):827-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2006.10.002. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006. PMID: 17113008 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical efficacy and safety of thoracoscopic talc pleurodesis in malignant pleural effusions.Chest. 2005 Sep;128(3):1431-5. doi: 10.1378/chest.128.3.1431. Chest. 2005. PMID: 16162739
-
Treatment of Malignant Pleural Effusions.Clin Chest Med. 2025 Jun;46(2):227-240. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2025.02.002. Clin Chest Med. 2025. PMID: 40484498 Review.
-
Talc pleurodesis in malignant pleural effusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021 May;69(5):832-842. doi: 10.1007/s11748-020-01549-2. Epub 2020 Nov 22. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 33222091
Cited by
-
The effect of pleural abrasion on the treatment of primary spontaneous pneumothorax: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 4;10(6):e0127857. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127857. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26042737 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent Large Volume Malignant Pleural Effusion in a Patient With Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cureus. 2021 Feb 27;13(2):e13593. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13593. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33815993 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive palliative interventions in advanced lung cancer.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2018 Jul;12(7):605-614. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2018.1486709. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2018. PMID: 29883216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the efficacy and advancements of medical pleurodesis: a comprehensive review of current research.Breathe (Sheff). 2024 Aug 27;20(2):240002. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0002-2024. eCollection 2024 Jun. Breathe (Sheff). 2024. PMID: 39193457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treating Recurrent Pleural Disease: A Review of Indications and Technique for Chemical Pleurodesis for the Interventional Radiologist.Semin Intervent Radiol. 2022 Aug 31;39(3):275-284. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1754349. eCollection 2022 Jun. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2022. PMID: 36062225 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Thoracic Society (2000) Management of malignant pleural effusions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 162: 1987–2001. - PubMed
-
- Martinez-Moragon E, Aparicio J, Sanchis J, Menendez R, Cruz Rogado M, et al. (1998) Malignant pleural effusion: prognostic factors for survival and response to chemical pleurodesis in a series of 120 cases. Respiration 65: 108–113. - PubMed
-
- Kastelik JA (2013) Management of malignant pleural effusion. Lung 191: 165–175. - PubMed
-
- Khaleeq G, Musani AI (2008) Emerging paradigms in the management of malignant pleural effusions. Respir Med 102: 939–948. - PubMed
-
- Roberts ME, Neville E, Berrisford RG, Antunes G, Ali NJ (2010) Management of a malignant pleural effusion: British Thoracic Society Pleural Disease Guideline 2010. Thorax 65 Suppl 2ii32–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

