Plasma concentration of platelet-derived microparticles is related to painful vaso-occlusive phenotype severity in sickle cell anemia
- PMID: 24475257
- PMCID: PMC3901744
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087243
Plasma concentration of platelet-derived microparticles is related to painful vaso-occlusive phenotype severity in sickle cell anemia
Abstract
High plasma level of microparticles (MPs) deriving mainly from erythrocytes and platelets has been detected in sickle cell anemia (SCA) patients. Flow cytometry was used to determine the concentration of MPs in two groups of SCA patients exhibiting marked differences in painful vaso-occlusive crisis rates [a non-severe group (n = 17) and a severe group (n = 12)], and in a control group composed of healthy subjects (n = 20). A 3- to 4-fold increase of total MP plasma concentration was detected in SCA patients. Higher platelet-derived MPs concentration was detected in the severe SCA group while erythrocyte-derived MPs concentration was increased in the non-severe SCA patient group only. Our results suggest that plasma concentration of MPs shed by platelets is a biomarker of the vaso-occlusive phenotype-related severity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
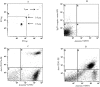

References
-
- Stuart MJ, Nagel RL (2004) Sickle-cell disease. Lancet 364: 1343–1360. - PubMed
-
- Wood KC, Hsu LL, Gladwin MT (2008) Sickle cell disease vasculopathy: a state of nitric oxide resistance. Free Radic Biol Med 44: 1506–1528. - PubMed
-
- Lamarre Y, Romana M, Lemonne N, Hardy-Dessources MD, Tarer V, et al... (2013) Alpha thalassemia protects sickle cell anemia patients from macro-albuminuria through its effects on red blood cell rheological properties. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

