Symmetric dimethyl arginine and N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase lysozimuria of proximal renal tubules as a target for nephrotoxicity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs
- PMID: 24475424
- PMCID: PMC3886170
- DOI: 10.5812/nephropathol.8989
Symmetric dimethyl arginine and N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase lysozimuria of proximal renal tubules as a target for nephrotoxicity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to determine the effect of initial therapy with some disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) (Methotrexate and Ketoprofen) on glomerular and tubular integrity in patients with Rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Objectives: To determine whether there is a change in clinical and laboratory indicators of renal function in course of the follow up of treatment and whether that change correlates with the dynamics of the quantity of enzymes excreted in urine and reactants of the acute phase.
Materials and methods: Using colorimetric method for determination of NAG, samples of 70 participants were examined (35 RA patients treated with Ketoprofen only, 35 RA patients treated with combined use of Methotrexate and Ketoprofen). The follow up was 5 time-intervals in the course of 24 weeks.
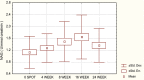
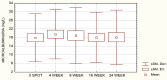
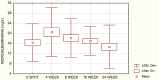
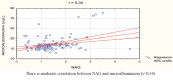
Results: There was moderate correlation between NAG and microalbuminuria (r=0,34) in the group of patients treated with Ketoprofen only, while statistically significant correlation (r=0,21) was seen in group of patients with combined use of Methotrexate and Ketoprofen. NAG enzymuria in size, number of patients registered, and time of appearance were greater and appears earlier in the group with the combined use of Methotrexate and Ketoprofen compared with the mono-therapy with Ketoprofen. Mean urinary NAG induction was increasing with the concomitant use of Methotrexate and Ketoprofen.
Conclusions: Methotrexate is more potent NAG inductor than Ketoprofen and provokes greater tubular enzymuria than Ketoprofen.
Keywords: Immunosuppressive drugs; N-acetyl-D-glucosaminidase; Rheumatoid arthritis; Symmetric dimethyl arginine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renal function in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with methotrexate and infliximab.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004 Jul-Aug;22(4):469-72. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004. PMID: 15301246
-
[Renal tubular dysfunction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis starting with low dose of methotrexate].Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2003 Aug;110(2):855-62. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2003. PMID: 14682224 Polish.
-
N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase urinary excretion as an early indicator of kidney dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis patients on low-dose methotrexate treatment.Br J Rheumatol. 1997 Jan;36(1):59-63. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.1.59. Br J Rheumatol. 1997. PMID: 9117176
-
Baricitinib inhibits structural joint damage progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-a comprehensive review.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 Jan 4;23(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02379-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33397481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Kidney involvement in rheumatoid arthritis].Reumatismo. 2003;55(2):76-85. doi: 10.4081/reumatismo.2003.76. Reumatismo. 2003. PMID: 12874640 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Advances in Optical Sensors of N-Acetyl-β-d-hexosaminidase (N-Acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase).Bioconjug Chem. 2022 Apr 20;33(4):544-554. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00057. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Bioconjug Chem. 2022. PMID: 35302753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of microalbuminuria as a predictor of subclinical cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis patients and its relation to disease activity.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Mar;37(3):623-630. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3849-5. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29063462
References
-
- Mellman I, Fuchs R, Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem . 1986;55:663–700. - PubMed
-
- Dos Santos AC, Colacciopo S, Dal Bo CM. Occupational exposure to lead, kidney function tests and blood pressure. Am J Int Med . 1994;26:635–43. - PubMed
-
- Shibasak T, Nakano H, Ohno I. Effect of pentoxifylline on CdCl -induced nephrotoxici-2ty in the rat. Biol Trace Elem Res . 1994;41:245–51. - PubMed
-
- Hong CY, Chia KS. Markers of diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complications . 1998;12:43–60. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources