The myxobacterial metabolite ratjadone A inhibits HIV infection by blocking the Rev/CRM1-mediated nuclear export pathway
- PMID: 24475978
- PMCID: PMC3910686
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-13-17
The myxobacterial metabolite ratjadone A inhibits HIV infection by blocking the Rev/CRM1-mediated nuclear export pathway
Abstract
Background: The nuclear export of unspliced and partially spliced HIV-1 mRNA is mediated by the recognition of a leucine-rich nuclear export signal (NES) in the HIV Rev protein by the host protein CRM1/Exportin1. This makes the CRM1-Rev complex an attractive target for the development of new antiviral drugs. Here we tested the anti-HIV efficacy of ratjadone A, a CRM1 inhibitor derived from myxobacteria.
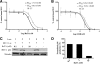
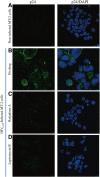
Results: Ratjadone A inhibits HIV infection in vitro in a dose-dependent manner with EC₅₀ values at the nanomolar range. The inhibitory effect of ratjadone A occurs around 12 hours post-infection and is specific for the Rev/CRM1-mediated nuclear export pathway. By using a drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS) assay we could demonstrate that ratjadone A interferes with the formation of the CRM1-Rev-NES complex by binding to CRM1 but not to Rev.
Conclusion: Ratjadone A exhibits strong anti-HIV activity but low selectivity due to toxic effects. Although this limits its potential use as a therapeutic drug, further studies with derivatives of ratjadones might help to overcome these difficulties in the future.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A synthetic HIV-1 Rev inhibitor interfering with the CRM1-mediated nuclear export.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 29;99(22):14440-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.212285299. Epub 2002 Oct 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12374846 Free PMC article.
-
ANP32A and ANP32B are key factors in the Rev-dependent CRM1 pathway for nuclear export of HIV-1 unspliced mRNA.J Biol Chem. 2019 Oct 18;294(42):15346-15357. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008450. Epub 2019 Aug 23. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31444273 Free PMC article.
-
Ratjadones inhibit nuclear export by blocking CRM1/exportin 1.Exp Cell Res. 2003 Jun 10;286(2):321-31. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(03)00100-9. Exp Cell Res. 2003. PMID: 12749860
-
[HIV-1 Rev and related inhibitors].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007 Apr;42(4):347-51. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17633198 Review. Chinese.
-
Nuclear export of proteins and drug resistance in cancer.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Apr 15;83(8):1021-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.12.016. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22209898 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral Compounds from Myxobacteria.Microorganisms. 2018 Jul 19;6(3):73. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms6030073. Microorganisms. 2018. PMID: 30029487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does Size Really Matter? Probing the Efficacy of Structural Reduction in the Optimization of Bioderived Compounds - A Computational "Proof-of-Concept".Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2018 Nov 23;16:573-586. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2018.11.005. eCollection 2018. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2018. PMID: 30546858 Free PMC article.
-
The nuclear export protein XPO1 - from biology to targeted therapy.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021 Mar;18(3):152-169. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-00442-4. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33173198 Review.
-
Emerging Therapeutic Modalities against COVID-19.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Aug 8;13(8):188. doi: 10.3390/ph13080188. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32784499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting of nucleo‑cytoplasmic transport factor exportin 1 in malignancy (Review).Med Int (Lond). 2021 Dec 28;2(1):2. doi: 10.3892/mi.2021.27. eCollection 2022 Jan-Feb. Med Int (Lond). 2021. PMID: 38938904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

