Cardiorespiratory function associated with dietary nitrate supplementation
- PMID: 24476472
- PMCID: PMC3909870
- DOI: 10.1139/apnm-2013-0263
Cardiorespiratory function associated with dietary nitrate supplementation
Abstract
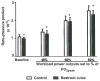
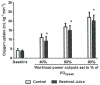
The advent of medical nutrition therapy and nutritional physiology affords the opportunity to link diet to specific cardiovascular mechanisms, suggesting novel treatments for cardiovascular disease. This study tests the hypothesis that beetroot juice increases the plasma nitric oxide (NO) concentration, which is associated with improvements in cardiorespiratory function at rest and during submaximal aerobic exercise. The subjects were 12 healthy, young adult, normotensive African-American females, with a body mass of 61 ± 2 kg, body fat of 28% ± 4%, and peak oxygen consumption of 26 ± 3 mL·kg(-1)·min(-1). The subjects were studied at rest and during cycle ergometer exercise at 40%, 60%, and 80% of peak oxygen consumption. Plasma NO concentration, respiratory quotient (RQ), minute ventilation, systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP and DBP), heart rate, and oxygen consumption were compared between isocaloric, isovolumetric placebo control orange juice and experimental beetroot juice treatments on separate days. The beetroot juice treatment increased plasma NO concentration and decreased oxygen consumption, SBP, and the heart rate-SBP product at rest and at 40%, 60%, and 80% of peak oxygen consumption in the absence of significant effects on RQ, minute ventilation, heart rate, and DBP. These findings suggest that, in healthy subjects, beetroot juice treatments increase plasma NO concentration and decrease cardiac afterload and myocardial oxygen demand at rest and during 3 submaximal levels of aerobic exercise. Future studies should determine the cellular and molecular mechanisms responsible for the improvement in cardiorespiratory function associated with dietary nitrate supplementation and whether they translate into better cardiovascular function and exercise tolerance in individuals with a compromised cardiovascular system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
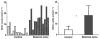
References
-
- Bailey SJ, Winyard P, Vanhatalo A, Blackwell JR, Dimenna FJ, Wilkerson DP, et al. Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of low-intensity exercise and enhances tolerance to high-intensity exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol. 2009;107(4):1144–1155. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00722.2009.. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Belardinelli R. Trimetazidine and the contractile response of dysfunctional myocardium in ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Rev Port Cardiol. 2000;19(Suppl 5):V35–V39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

