Comprehensive molecular characterization of urothelial bladder carcinoma
- PMID: 24476821
- PMCID: PMC3962515
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12965
Comprehensive molecular characterization of urothelial bladder carcinoma
Abstract
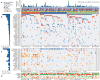
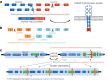
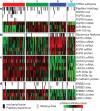
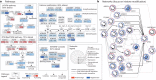
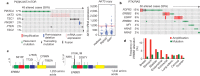
Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder is a common malignancy that causes approximately 150,000 deaths per year worldwide. So far, no molecularly targeted agents have been approved for treatment of the disease. As part of The Cancer Genome Atlas project, we report here an integrated analysis of 131 urothelial carcinomas to provide a comprehensive landscape of molecular alterations. There were statistically significant recurrent mutations in 32 genes, including multiple genes involved in cell-cycle regulation, chromatin regulation, and kinase signalling pathways, as well as 9 genes not previously reported as significantly mutated in any cancer. RNA sequencing revealed four expression subtypes, two of which (papillary-like and basal/squamous-like) were also evident in microRNA sequencing and protein data. Whole-genome and RNA sequencing identified recurrent in-frame activating FGFR3-TACC3 fusions and expression or integration of several viruses (including HPV16) that are associated with gene inactivation. Our analyses identified potential therapeutic targets in 69% of the tumours, including 42% with targets in the phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase/AKT/mTOR pathway and 45% with targets (including ERBB2) in the RTK/MAPK pathway. Chromatin regulatory genes were more frequently mutated in urothelial carcinoma than in any other common cancer studied so far, indicating the future possibility of targeted therapy for chromatin abnormalities.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 DE019713/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143866/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143843/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003079/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069768/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143835/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143845/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143799/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA144025/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA126554/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA180951/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143840/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

