Infant feeding patterns in families with a diabetes history - observations from The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) birth cohort study
- PMID: 24477208
- PMCID: PMC4162845
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980013003054
Infant feeding patterns in families with a diabetes history - observations from The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) birth cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the association between diabetes family history and infant feeding patterns.
Design: Data on breast-feeding duration and age at first introduction of cow's milk and gluten-containing cereals were collected in 3-month intervals during the first 24 months of life.
Setting: Data from the multicentre TEDDY (The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young) study, including centres in the USA, Sweden, Finland and Germany.
Subjects: A total of 7026 children, including children with a mother with type 1 diabetes (T1D; n 292), gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM; n 404) or without diabetes but with a father and/or sibling with T1D (n 464) and children without diabetes family history (n 5866).
Results: While exclusive breast-feeding ended earlier and cow's milk was introduced earlier in offspring of mothers with T1D and GDM, offspring of non-diabetic mothers but a father and/or sibling with T1D were exclusively breast-fed longer and introduced to cow's milk later compared with infants without diabetes family history. The association between maternal diabetes and shorter exclusive breast-feeding duration was attenuated after adjusting for clinical variables (delivery mode, gestational age, Apgar score and birth weight). Country-specific analyses revealed differences in these associations, with Sweden showing the strongest and Finland showing no association between maternal diabetes and breast-feeding duration.
Conclusions: Family history of diabetes is associated with infant feeding patterns; however, the associations clearly differ by country, indicating that cultural differences are important determinants of infant feeding behaviour. These findings need to be considered when developing strategies to improve feeding patterns in infants with a diabetes family history.
Figures

 , father/sib with T1D;
, father/sib with T1D;  , mother with GDM;
, mother with GDM;  , mother with T1D;
, mother with T1D;  , no diabetes family history), all participating countries: The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) study (sib, sibling; T1D, type 1 diabetes; GDM, gestational diabetes mellitus)
, no diabetes family history), all participating countries: The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) study (sib, sibling; T1D, type 1 diabetes; GDM, gestational diabetes mellitus)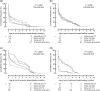
 , father/sib with T1D;
, father/sib with T1D;  , mother with GDM;
, mother with GDM;  , mother with T1D;
, mother with T1D;  , no diabetes family history): The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) study (sib, sibling; T1D, type 1 diabetes; GDM, gestational diabetes mellitus)
, no diabetes family history): The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) study (sib, sibling; T1D, type 1 diabetes; GDM, gestational diabetes mellitus)References
-
- Dewey KG, Heinig MJ, Nommsen LA et al. (1992) Growth of breast-fed and formula-fed infants from 0 to 18 months: the DARLING Study. Pediatrics 89, 1035–1041. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (2002) Infant and young child nutrition. Global strategy on infant and young child feeding http://apps.who.int/gb/archive/pdf_files/WHA55/ea5515.pdf (accessed October 2011).
-
- UNICEF (2009) Infant and young child feeding (2000–2007). http://www.childinfo.org/breastfeeding_countrydata.php(accessedOctober2011).
-
- Scott JA & Binns CW (1999) Factors associated with the initiation and duration of breastfeeding: a review of the literature. Breastfeed Rev 7, 5–16. - PubMed
-
- Hummel S, Winkler C, Schoen S et al et al. (2007) Breast-feeding habits in families with type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med 24, 671–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UC4 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK63790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200700014C/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK63863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK63861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK63836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK63865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK095300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 63829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4DK095300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK63821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

