Signalling between microvascular endothelium and cardiomyocytes through neuregulin
- PMID: 24477642
- PMCID: PMC3989448
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvu021
Signalling between microvascular endothelium and cardiomyocytes through neuregulin
Abstract
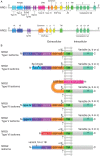
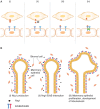
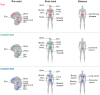
Heterocellular communication in the heart is an important mechanism for matching circulatory demands with cardiac structure and function, and neuregulins (Nrgs) play an important role in transducing this signal between the hearts' vasculature and musculature. Here, we review the current knowledge regarding Nrgs, explaining their roles in transducing signals between the heart's microvasculature and cardiomyocytes. We highlight intriguing areas being investigated for developing new, Nrg-mediated strategies to heal the heart in acquired and congenital heart diseases, and note avenues for future research.
Keywords: ErbB; Heart; Heterocellular communication; Neuregulin.
Figures
References
-
- Peles E, Yarden Y. Neu and its ligands: from an oncogene to neural factors. BioEssays News Rev Mol Cell Dev Biol. 1993;15:815–824. - PubMed
-
- Carraway KL, III, Weber JL, Unger MJ, Ledesma J, Yu N, Gassmann M, et al. Neuregulin-2, a new ligand of ErbB3/ErbB4-receptor tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1997;387:512–516. - PubMed
-
- Harari D, Tzahar E, Romano J, Shelly M, Pierce JH, Andrews GC, et al. Neuregulin-4: a novel growth factor that acts through the ErbB-4 receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncogene. 1999;18:2681–2689. - PubMed
-
- Hidalgo A, Kinrade EF, Georgiou M. The Drosophila neuregulin vein maintains glial survival during axon guidance in the CNS. Dev Cell. 2001;1:679–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

