Impact of surfactant protein D, interleukin-5, and eosinophilia on Cryptococcosis
- PMID: 24478083
- PMCID: PMC3911392
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00855-13
Impact of surfactant protein D, interleukin-5, and eosinophilia on Cryptococcosis
Abstract
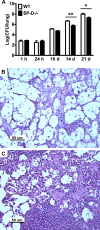
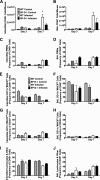
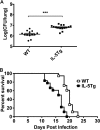
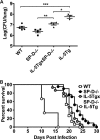
Cryptococcus neoformans is an opportunistic fungal pathogen that initiates infection following inhalation. As a result, the pulmonary immune response provides a first line of defense against C. neoformans. Surfactant protein D (SP-D) is an important regulator of pulmonary immune responses and is typically host protective against bacterial and viral respiratory infections. However, SP-D is not protective against C. neoformans. This is evidenced by previous work from our laboratory demonstrating that SP-D-deficient mice infected with C. neoformans have a lower fungal burden and live longer than wild-type (WT) control animals. We hypothesized that SP-D alters susceptibility to C. neoformans by dysregulating the innate pulmonary immune response following infection. Thus, inflammatory cells and cytokines were compared in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from WT and SP-D(-/-) mice after C. neoformans infection. Postinfection, mice lacking SP-D have reduced eosinophil infiltration and interleukin-5 (IL-5) in lung lavage fluid. To further explore the interplay of SP-D, eosinophils, and IL-5, mice expressing altered levels of eosinophils and/or IL-5 were infected with C. neoformans to assess the role of these innate immune mediators. IL-5-overexpressing mice have increased pulmonary eosinophilia and are more susceptible to C. neoformans infection than WT mice. Furthermore, susceptibility of SP-D(-/-) mice to C. neoformans infection could be restored to the level of WT mice by increasing IL-5 and eosinophils by crossing the IL-5-overexpressing mice with SP-D(-/-) mice. Together, these studies support the conclusion that SP-D increases susceptibility to C. neoformans infection by promoting C. neoformans-driven pulmonary IL-5 and eosinophil infiltration.
Figures

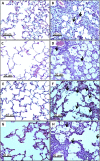
References
-
- Jain AV, Zhang Y, Fields WB, McNamara DA, Choe MY, Chen Gh Erb-Downward J, Osterholzer JJ, Toews GB, Huffnagle GB, Olszewski MA. 2009. Th2 but Not Th1 immune bias results in altered lung functions in a murine model of pulmonary Cryptococcus neoformans Infection. Infect. Immun. 77:5389–5399. 10.1128/IAI.00809-09 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muller U, Stenzel W, Kohler G, Werner C, Polte T, Hansen G, Schutze N, Straubinger RK, Blessing M, McKenzie AN, Brombacher F, Alber G. 2007. IL-13 induces disease-promoting type 2 cytokines, alternatively activated macrophages and allergic inflammation during pulmonary infection of mice with Cryptococcus neoformans. J. Immunol. 179:5367–5377 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

