Spinal noradrenergic modulation and the role of the alpha-2 receptor in the antinociceptive effect of intrathecal nefopam in the formalin test
- PMID: 24478897
- PMCID: PMC3903796
- DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.23
Spinal noradrenergic modulation and the role of the alpha-2 receptor in the antinociceptive effect of intrathecal nefopam in the formalin test
Abstract
Background: Nefopam has shown an analgesic effect on acute pain including postoperative pain. The reuptake of monoamines including serotonin and noradrenaline has been proposed as the mechanism of the analgesic action of nefopam, but it remains unclear. Although alpha-adrenergic agents are being widely used in the perioperative period, the role of noradrenergic modulation in the analgesic effect of nefopam has not been fully addressed.
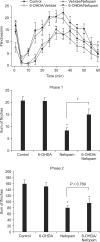
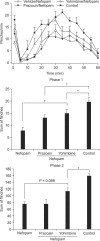
Methods: Changes in the antinociceptive effect of intrathecal (i.t.) nefopam against formalin-elicited flinching responses were explored in Sprague-Dawley rats pretreated with i.t. 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), which depletes spinal noradrenaline. In addition, antagonism to the effect of nefopam by prazosin and yohimbine was evaluated to further elucidate the antinociceptive mechanism of i.t. nefopam.
Results: Pretreatment with i.t. 6-OHDA alone did not alter the flinching responses in either phase of the formalin test, while it attenuated the antinociceptive effect of i.t. nefopam significantly during phase 1, but not phase 2. The antagonist of the alpha-2 receptor, but not the alpha-1 receptor, reduced partially, but significantly, the antinociceptive effect of i.t. nefopam during phase 1, but not during phase 2.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that spinal noradrenergic modulation plays an important role in the antinociceptive effect of i.t. nefopam against formalin-elicited acute initial pain, but not facilitated pain, and this action involves the spinal alpha-2 but not the alpha-1 receptor.
Keywords: alpha-2 receptor; formalin; nefopam; noradrenergic system; spinal cord.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Spinal Dopaminergic Transmission in the Analgesic Effect of Nefopam on Rat Inflammatory Pain.Korean J Pain. 2016 Jul;29(3):164-71. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.3.164. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Korean J Pain. 2016. PMID: 27413481 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive effect of intrathecal nefopam and interaction with morphine in formalin-induced pain of rats.Korean J Pain. 2013 Jan;26(1):14-20. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.1.14. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Korean J Pain. 2013. PMID: 23342202 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive effects of nefopam modulating serotonergic, adrenergic, and glutamatergic neurotransmission in the spinal cord.Neurosci Lett. 2020 Jul 13;731:135057. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135057. Epub 2020 May 23. Neurosci Lett. 2020. PMID: 32450186
-
Intrathecal nefopam-induced antinociception through activation of descending serotonergic projections involving spinal 5-HT7 but not 5-HT3 receptors.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Feb 5;587:120-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.12.040. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 25534502
-
Antinociceptive effects of nefopam activating descending serotonergic modulation via 5-HT2 receptors in the nucleus raphe magnus.Eur J Pain. 2024 Feb;28(2):252-262. doi: 10.1002/ejp.2173. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Eur J Pain. 2024. PMID: 37615256
Cited by
-
Anti-allodynic effect of intrathecal processed Aconitum jaluense is associated with the inhibition of microglial activation and P2X7 receptor expression in spinal cord.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Jul 13;16:214. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1201-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27411500 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid sparing effect and safety of nefopam in patient controlled analgesia after laparotomy: A randomized, double blind study.J Int Med Res. 2016 Aug;44(4):844-54. doi: 10.1177/0300060516650783. Epub 2016 Jun 29. J Int Med Res. 2016. PMID: 27358262 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
What do monoamines do in pain modulation?Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2016 Jun;10(2):143-8. doi: 10.1097/SPC.0000000000000207. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2016. PMID: 27043287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of the spinal 5-HT7 receptor and p-ERK pathway in the carrageenan inflammatory pain of rats.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2015 Apr;68(2):170-4. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2015.68.2.170. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2015. PMID: 25844136 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Spinal Dopaminergic Transmission in the Analgesic Effect of Nefopam on Rat Inflammatory Pain.Korean J Pain. 2016 Jul;29(3):164-71. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.3.164. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Korean J Pain. 2016. PMID: 27413481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fuller RW, Snoddy HD. Evaluation of nefopam as a monoamine uptake inhibitor in vivo in mice. Neuropharmacology. 1993;32:995–999. - PubMed
-
- Rosland JH, Hole K. The effect of nefopam and its enantiomers on the uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline and dopamine in crude rat brain synaptosomal preparations. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1990;42:437–438. - PubMed
-
- Vonvoigtlander PF, Lewis RA, Neff GL, Triezenberg HJ. Involvement of biogenic amines with the mechanisms of novel analgesics. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1983;7:651–656. - PubMed
-
- Esposito E, Romandini S, Merlo-Pich E, Mennini T, Samanin R. Evidence of the involvement of dopamine in the analgesic effect of nefopam. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986;128:157–164. - PubMed
-
- Hunskaar S, Fasmer OB, Broch OJ, Hole K. Involvement of central serotonergic pathways in nefopam-induced antinociception. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987;138:77–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

