Oxytocin in pregnancy and the postpartum: relations to labor and its management
- PMID: 24479112
- PMCID: PMC3902863
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2014.00001
Oxytocin in pregnancy and the postpartum: relations to labor and its management
Abstract
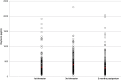
The purpose of this study was to examine variations in endogenous oxytocin levels in pregnancy and postpartum state. We also explored the associations between delivery variables and oxytocin levels. A final sample of 272 mothers in their first trimester of pregnancy was included for the study. Blood samples were drawn during the first trimester and third trimester of pregnancy and at 8 weeks postpartum. Socio-demographic data were collected at each time point and medical files were consulted for delivery details. In most women, levels of circulating oxytocin increased from the first to third trimester of pregnancy followed by a decrease in the postpartum period. Oxytocin levels varied considerably between individuals, ranging from 50 pg/mL to over 2000 pg/mL. Parity was the main predictor of oxytocin levels in the third trimester of pregnancy and of oxytocin level changes from the first to the third trimester of pregnancy. Oxytocin levels in the third trimester of pregnancy predicted a self-reported negative labor experience and increased the chances of having an epidural. Intrapartum exogenous oxytocin was positively associated with levels of oxytocin during the postpartum period. Our exploratory results suggest that circulating oxytocin levels during the third trimester of pregnancy may predict the type of labor a woman will experience. More importantly, the quantity of intrapartum exogenous oxytocin administered during labor predicted plasma oxytocin levels 2 months postpartum, suggesting a possible long-term effect of this routine intervention, the consequences of which are largely unknown.
Keywords: epidural; labor; oxytocin; pregnancy; syntocinon.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

