Declining malaria in Africa: improving the measurement of progress
- PMID: 24479555
- PMCID: PMC3930350
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-39
Declining malaria in Africa: improving the measurement of progress
Abstract
The dramatic escalation of malaria control activities in Africa since the year 2000 has increased the importance of accurate measurements of impact on malaria epidemiology and burden. This study presents a systematic review of the emerging published evidence base on trends in malaria risk in Africa and argues that more systematic, timely, and empirically-based approaches are urgently needed to track the rapidly evolving landscape of transmission.
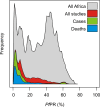
Figures

References
-
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2012. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012. p. 259.
-
- RBMP. The Global Malaria Action Plan for a Malaria Free World. Geneva: Roll Back Malaria Partnership, World Health Organization; 2008.
-
- BMGF. Annual Letter from Bill Gates 2013. Seattle, WA: The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation; 2013.
-
- WHO. Disease Surveillance for Malaria Control. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012. p. 65.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

