Brucella arteritis: clinical manifestations, treatment, and prognosis
- PMID: 24480149
- PMCID: PMC4498663
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70270-6
Brucella arteritis: clinical manifestations, treatment, and prognosis
Abstract
Brucellosis is the most common bacterial zoonosis, and causes a considerable burden of disease in endemic countries. Cardiovascular involvement is the main cause of mortality due to infection with Brucella spp, and most commonly manifests as endocarditis, peripheral and cerebrovascular aneurysms, or arterial and venous thromboses. We report a case of brucellosis presenting as bacteraemia and aortic endarteritis 18 years after the last known exposure to risk factors for brucella infection. The patient was treated with doxycycline, rifampicin, and gentamicin, and underwent surgical repair of a penetrating aortic ulcer, with a good clinical recovery. We review the signs and symptoms, diagnostic approach, prognosis, and treatment of brucella arteritis. We draw attention to the absence of consensus about the optimum therapy for vascular brucellosis, and the urgent need for additional studies and renewed scientific interest in this major pathogen.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
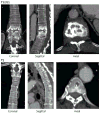


Comment in
-
Brucellar aortitis and brucellar spondylitis.Lancet Infect Dis. 2015 Feb;15(2):145-6. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)71027-8. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25749059 No abstract available.
References
-
- Franco MP, Mulder M, Gilman RH, Smits HL. Human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:775–786. - PubMed
-
- Buzgan T, Karahocagil MK, Irmak H, et al. Clinical manifestations and complications in 1028 cases of brucellosis: a retrospective evaluation and review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14:e469–e478. - PubMed
-
- Pappas G, Akritidis N, Bosilkovski M, Tsianos E. Brucellosis. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2325–2336. - PubMed
-
- Al-Tawfiq JA. Therapeutic options for human brucellosis. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008;6:109–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

