Immunoneuropathogenesis of HIV-1 clades B and C: role of redox expression and thiol modification
- PMID: 24480751
- PMCID: PMC4211896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.12.025
Immunoneuropathogenesis of HIV-1 clades B and C: role of redox expression and thiol modification
Abstract
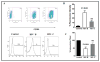
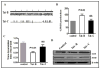
Previous studies have shown that, during infection, HIV-1 clade B and clade C differentially contribute to the neuropathogenesis and development of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HANDs). The low-molecular-weight tripeptide glutathione (GSH) alters the redox balance and leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species, which play a significant role in the neuropathogenesis of HANDs. We hypothesized that the HIV-1 clade B and clade C viruses and their respective Tat proteins exert differential effects on monocyte-derived immature dendritic cells (IDCs) and neuroblastoma cells (SK-N-MC) by redox activation, which leads to immunoneuropathogenesis. The GSH/GSSG ratio and mRNA expression levels and protein modification of glutathione synthetase (GSS), glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPx1), superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1), and catalase (CAT) were analyzed in IDCs infected with HIV-1 clade B or clade C as well as in cells treated with the respective Tat proteins. The results indicated that HIV-1 clade B virus and its Tat protein significantly increased the production of reactive oxygen species and reduced the GSH/GSSG ratio and subsequent downregulation of gene expression and protein modification of GSS, GPx1, SOD1, and CAT compared to infection with the clade C virus or treatment with the clade C Tat protein. Thus, our studies demonstrate that HIV-1 clades B and C exert differential effects of redox expression and thiol modification. HIV-1 clade B potentially induces oxidative stress, leading to more immunoneuropathogenesis than infection with HIV-1 clade C.
Keywords: Dendritic cells; Free radicals; Glutathione; HIV-1 clade B; HIV-1 clade C; Neuron; Oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Robertson DL, Anderson JP, Bradac JA, Carr JK, Foley B, Funkhouser RK, Gao F, Hahn BH, Kalish ML, Kuiken C, Learn GH, Leitner T, McCutchan F, Osmanov S, Peeters M, Pieniazek D, Salminen M, Sharp PM, Wolinsky S, Korber B. HIV-1 nomenclature proposal. Science. 2000;288:55–56. - PubMed
-
- Osmanov S, Pattou C, Walker N, Schwardländer B, Esparza J. Estimated global distribution and regional spread of HIV-1 genetic subtypes in the year 2000. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2000;29:184–190. - PubMed
-
- Korber B, Kuiken C, Foley B, Hanh B, McCutchan F, Mellors J, Sodroski J. A compilation and analysis of nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Los Alamos, NM: Theoretical Biology and Biophysics Group, Los Alamos National Laboratory; 1998. Human retroviruses and AIDS.
-
- Rambaut A, Robertson DL, Pybus OG, Peeters M, Holmes EC. Human immunodeficiency virus. Phylogeny and the origin of HIV-1. Nature. 2001;410:1047–1048. - PubMed
-
- Myers G, MacInnes K, Korber B. The emergence of simian/human immunodeficiency viruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992;8:373–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

