Effect of beetroot juice supplementation on aerobic response during swimming
- PMID: 24481133
- PMCID: PMC3942720
- DOI: 10.3390/nu6020605
Effect of beetroot juice supplementation on aerobic response during swimming
Abstract
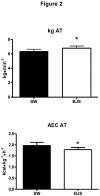
The beneficial effects of beetroot juice supplementation (BJS) have been tested during cycling, walking, and running. The purpose of the present study was to investigate whether BJS can also improve performance in swimmers. Fourteen moderately trained male master swimmers were recruited and underwent two incremental swimming tests randomly assigned in a pool during which workload, oxygen uptake (VO₂), carbon dioxide production (VCO₂), pulmonary ventilation (VE), and aerobic energy cost (AEC) of swimming were measured. One was a control swimming test (CSW) and the other a swimming test after six days of BJS (0.5 l/day organic beetroot juice containing about 5.5 mmol of NO₃⁻). Results show that workload at anaerobic threshold was significantly increased by BJS as compared to the CSW test (6.3 ± 1 and 6.7 ± 1.1 kg during the CSW and the BJS test respectively). Moreover, AEC was significantly reduced during the BJS test (1.9 ± 0.5 during the SW test vs. 1.7 ± 0.3 kcal·kg⁻¹1·h⁻¹ during the BJS test). The other variables lacked a statistically significant effect with BJS. The present investigation provides evidence that BJS positively affects performance of swimmers as it reduces the AEC and increases the workload at anaerobic threshold.
Figures

Similar articles
-
No Effect of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on 100-m and 200-m Swimming Performance in Moderately Trained Swimmers.Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2019 Jul 1;14(6):706-710. doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2018-0654. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2019. PMID: 30427246 Clinical Trial.
-
Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of walking and running: a placebo-controlled study.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011 Mar;110(3):591-600. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01070.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 11. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011. PMID: 21071588 Clinical Trial.
-
No individual or combined effects of caffeine and beetroot-juice supplementation during submaximal or maximal running.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018 Jul;43(7):697-703. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2017-0547. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018. PMID: 29444414 Clinical Trial.
-
Beetroot juice does not enhance altitude running performance in well-trained athletes.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2015 Jun;40(6):590-5. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2014-0470. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2015. PMID: 25942474 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of dietary nitrate-rich beetroot juice supplementation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021 Apr;42:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.01.035. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021. PMID: 33745600
Cited by
-
Effects of Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation and Exercise on Cardiovascular Function in Healthy Men in Preliminary Study: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled, and Crossover Trial.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Jun 21;12(13):1240. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12131240. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38998775 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of acute beetroot juice intake on performance, maximal oxygen uptake, and ventilatory efficiency in well-trained master rowers: a randomized, double-blinded crossover study.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2024 Dec;21(1):2373170. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2024.2373170. Epub 2024 Jul 2. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38953606 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nitrate Supplementation Combined with a Running Training Program Improved Time-Trial Performance in Recreationally Trained Runners.Sports (Basel). 2019 May 21;7(5):120. doi: 10.3390/sports7050120. Sports (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31117193 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of beetroot juice (Beta Vulgaris L.) supplementation on ṼO2max of youth soccer athletes.J Public Health Afr. 2022 Dec 7;13(Suppl 2):2406. doi: 10.4081/jphia.2022.2406. eCollection 2022 Dec 7. J Public Health Afr. 2022. PMID: 37497138 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Dietary Antioxidants on Sport Performance: A Review.Sports Med. 2015 Jul;45(7):939-55. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0323-x. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 25790792 Review.
References
-
- Appel L.J., Moore T.J., Obarzanek E., Vollmer W.M., Svetkey L.P., Sacks F.M., Bray G.A., Vogt T.M., Cutler J.A., Windhauser M.M., et al. A clinical trial of dietary patterns on blood pressure. DASH Collaborative Research Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;336:1117–1124. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199704173361601. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bailey S.J., Winyard P., Vanhatalo A., Blackwell J.R., Dimenna F.J., Wilkerson D.P., Tarr J., Benjamin N., Jones A.M. Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of low-intensity exercise and enhances tolerance ho high-intensity exercise in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009;107:1144–1155. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00722.2009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

