Morphological changes in Proteus mirabilis O18 biofilm under the influence of a urease inhibitor and a homoserine lactone derivative
- PMID: 24481535
- PMCID: PMC3931938
- DOI: 10.1007/s00203-014-0952-8
Morphological changes in Proteus mirabilis O18 biofilm under the influence of a urease inhibitor and a homoserine lactone derivative
Abstract
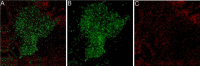
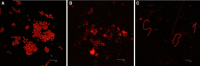
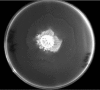
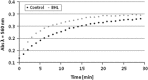
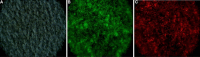
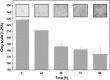
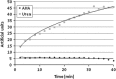
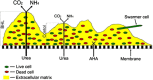
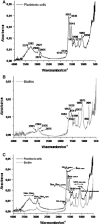
Proteus mirabilis is a pathogenic gram-negative bacterium that frequently causes kidney infections, typically established by ascending colonization of the urinary tract. The present study is focused on ureolytic activity and urease inhibition in biofilms generated by P. mirabilis O18 cells. Confocal microscopy revealed morphological alterations in biofilms treated with urea and a urease inhibitor (acetohydroxamic acid, AHA), as some swarmer cells were found to protrude from the biofilm. The presence of a quorum-sensing molecule (N-butanoyl homoserine lactone, BHL) increased biofilm thickness and its ureolytic activity. Laser interferometric determination of diffusion showed that urea easily diffuses through P. mirabilis biofilm, while AHA is blocked. This may suggest that the use of urease inhibitors in CAUTIs may by less effective than in other urease-associated infections. Spectroscopic studies revealed differences between biofilm and planktonic cells indicating that polysaccharides and nucleic acids are involved in extracellular matrix and biofilm formation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of urease inhibitors on the encrustation of urethral catheters.Urol Res. 1998;26(4):275-9. doi: 10.1007/s002400050057. Urol Res. 1998. PMID: 9760002
-
Influence of quorum sensing signal molecules on biofilm formation in Proteus mirabilis O18.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2012 Jan;57(1):53-60. doi: 10.1007/s12223-011-0091-4. Epub 2011 Dec 24. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2012. PMID: 22198843 Free PMC article.
-
Allicin from garlic inhibits the biofilm formation and urease activity of Proteus mirabilis in vitro.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2015 May;362(9):fnv049. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnv049. Epub 2015 Apr 2. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25837813
-
Proteus mirabilis Biofilm: Development and Therapeutic Strategies.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Aug 14;10:414. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00414. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32923408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of Proteus mirabilis in Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections.Urol Int. 2021;105(5-6):354-361. doi: 10.1159/000514097. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Urol Int. 2021. PMID: 33691318 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of Proteus mirabilis Infection.EcoSal Plus. 2018 Feb;8(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0009-2017. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0009-2017. EcoSal Plus. 2018. PMID: 29424333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Proteus mirabilis cell wall features in biofilm formation.Arch Microbiol. 2016 Nov;198(9):877-84. doi: 10.1007/s00203-016-1249-x. Epub 2016 Jun 4. Arch Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27262948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arabski M, Wasik S, Dworecki K, Kaca W. Laser interferometric and cultivation methods for measurement of colistin/ampicilin and saponin interactions with smooth and rough of Proteus mirabilis lipopolysaccharides and cells. J Microbiol Methods. 2009;77(2):178–183. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2009.01.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arabski M, Wasik S, Drulis-Kawa Z, Grzeskiewicz H, Gubernator J, Kaca W (2012) Laser interferometric determination of liposomes diffusion through artificial membranes In: Interferometry–research and applications in science and technology. ISBN 978-953-51-0403-2, 2012
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

