Assessment of the kappa opioid agonist, salvinorin A, as a punisher of drug self-administration in monkeys
- PMID: 24481567
- PMCID: PMC4074245
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-014-3436-2
Assessment of the kappa opioid agonist, salvinorin A, as a punisher of drug self-administration in monkeys
Abstract
Rationale: Drugs can function as punishers. However, work on the study of drugs as punishers is limited, as is the range of compounds known to function as punishers. Kappa opioid agonists, which have received much experimental attention as potential therapeutics for drug abuse, reportedly produce aversive effects. However, kappa agonists have yet to be tested as punishers of behavior.
Objective: The goal of the current study was to determine if a kappa agonist could function as a punisher of drug self-administration.
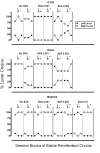
Method: In separate experiments, monkeys were allowed to choose in a two-lever choice design between intravenous injections of equal doses of either cocaine (0.1 mg/kg/injection on each lever) or remifentanil (0.1 μg/kg/injection on each lever) when one of the two options was mixed with various doses of the kappa agonist, salvinorin A.
Results: Choice for the cocaine and remifentanil options that were combined with salvinorin A decreased as a function of salvinorin A dose in all monkeys. However, operant response rates were not systematically affected by salvinorin A administration.
Conclusion: The present findings demonstrate that the kappa agonist, salvinorin A, can punish self-administration of a psychotimulant, cocaine, and a mu opioid, remifentanil. In consideration of these findings, it may be possible to curtail the abuse of some drugs by contingently delivering kappa agonists (e.g., as combination formularies for prescription medications).
Figures


References
-
- Azrin NH, Holz WC. Punishment. In: Honig WK, editor. Operant behavior: areas of research and application. Prentice-Hall Inc.; Englewood Cliffs: 1966. pp. 380–447.
-
- Butelman ER, Mandau M, Tidgewell K, Prisinzano TE, Yuferov V, Kreek MJ. Effects of salvinorin A, a kappa opioid hallucinogen, on a neuroendocrine biomarker assay in nonhuman primates with high kappa receptor homology in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;320:300–306. - PubMed
-
- Carlezon WA, Jr, Be guin C, DiNieri JA, Baumann MH, Richards MR, Todtenkopf MS, Rothman RB, Ma Z, Lee DY, Cohen BM. Depressive-like effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A on behavior and neurochemistry in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;316:440–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

