Effect of time from diagnosis to start of radiotherapy on children with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma
- PMID: 24482196
- PMCID: PMC4378861
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.24971
Effect of time from diagnosis to start of radiotherapy on children with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma
Abstract
Background: Children with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) continue to have poor outcomes, and radiotherapy (RT) is the only temporarily effective treatment. In this retrospective analysis, we studied the effect of time from diagnosis to start of RT on event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) in children with DIPG.
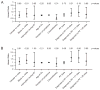
Methods: Records of children (n = 95) with DIPG treated with RT at a single institution between April 1999 and September 2009 were analyzed. RT was delivered at doses of 54.0-55.8 Gy at 1.8 Gy per fraction, and children were followed prospectively. The effect of gender, race, interruption during treatment course, age at diagnosis, duration of symptoms prior to diagnosis, use of protocol-based chemotherapy, and time from diagnosis to initiation of RT on EFS and OS was assessed by the Cox proportional hazards model.
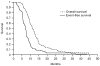
Results: Time as a continuous variable from diagnosis to start of RT did not affect outcome. Time dichotomized to ≤14 days significantly affected OS (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.70, P = 0.014) and race other than white or black affected EFS (HR = 2.32, P = 0.017). The 95 patients had a 6-month EFS and OS of 60 ± 5% and 94.7 ± 2.3%, respectively, and a 12-month EFS and OS of 11.6 ± 3.1% and 49.5 ± 5%, respectively.
Conclusions: Time as a continuous variable did not affect OS or EFS in our cohort; however, children treated within 2 weeks of diagnosis had poor outcomes. Although rapid initiation of RT is desirable, our findings do not support intensive efforts aimed at shortening delays from diagnosis to start of RT.
Keywords: diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma; outcomes; radiotherapy; timing.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hargrave D, Bartels U, Bouffet E. Diffuse brainstem glioma in children: critical review of clinical trials. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7(3):241–248. - PubMed
-
- Bouffet E, Raquin M, Doz F, et al. Radiotherapy followed by high dose busulfan and thiotepa: a prospective assessment of high dose chemotherapy in children with diffuse pontine gliomas. Cancer. 2000;88(3):685–692. - PubMed
-
- Chassot A, Canale S, Varlet P, et al. Radiotherapy with concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide in children with newly diagnosed diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. J Neurooncol. 2012;106(2):399–407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

