Exome sequencing links corticospinal motor neuron disease to common neurodegenerative disorders
- PMID: 24482476
- PMCID: PMC4157572
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1247363
Exome sequencing links corticospinal motor neuron disease to common neurodegenerative disorders
Abstract
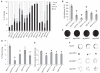
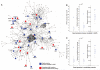
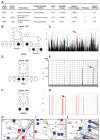
Hereditary spastic paraplegias (HSPs) are neurodegenerative motor neuron diseases characterized by progressive age-dependent loss of corticospinal motor tract function. Although the genetic basis is partly understood, only a fraction of cases can receive a genetic diagnosis, and a global view of HSP is lacking. By using whole-exome sequencing in combination with network analysis, we identified 18 previously unknown putative HSP genes and validated nearly all of these genes functionally or genetically. The pathways highlighted by these mutations link HSP to cellular transport, nucleotide metabolism, and synapse and axon development. Network analysis revealed a host of further candidate genes, of which three were mutated in our cohort. Our analysis links HSP to other neurodegenerative disorders and can facilitate gene discovery and mechanistic understanding of disease.
Figures
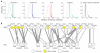
Comment in
-
Genetics. A unified process for neurological disease.Science. 2014 Jan 31;343(6170):497-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1250172. Science. 2014. PMID: 24482474 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics: Exome sequencing sheds light on hereditary spastic paraplegia.Nat Rev Neurol. 2014 Mar;10(3):124. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2014.27. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24566998 No abstract available.
-
Will next-generation sequencing also take us to the next level of understanding disease mechanisms?Mov Disord. 2014 Jun;29(7):868. doi: 10.1002/mds.25905. Epub 2014 May 5. Mov Disord. 2014. PMID: 24797999 No abstract available.
References
-
-
See supplementary text available on Science Online.
-
-
- D’Amico A, et al. Neurology. 2004;62:2138–2139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- P41 GM103504/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 NS048453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CO012400/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01HD070494/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS048453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS041537/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052455/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD070494/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CO-12400/CO/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011/PHS HHS/United States
- R01NS041537/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS052455/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

