Hypoxia induced changes of SePP1 expression in rat preadipocytes and its impact on vascular fibroblasts
- PMID: 24482687
- PMCID: PMC3902239
Hypoxia induced changes of SePP1 expression in rat preadipocytes and its impact on vascular fibroblasts
Abstract
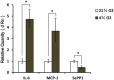
Human adipose tissues secret a lot of cytokines involved in physiological and pathological activities. Inflammation around blood vessels is positively related to the severity of atherosclerosis. This study was to investigate the impact of adipokine SePP1 on vascular fibroblasts (VF) under a hypoxia condition might provide new evidence and methods for treatment of atherosclerosis. The mRNA and protein expression of IL-6, MCP-1 and SePP1 were detected in preadipocytes under normoxic (21% O2) and hyperoxic (4% O2) conditions, and the impact of IL-6, MCP-1 and SePP1 on VF was investigated. The preadipocytes were cultured under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Then, the cell growth, and the mRNA and protein expression of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, MCP-1 and SePP1) were detected. The VF were cultured in the medium collected from preadipocytes maintained under hypoxic and normoxic conditions, and the phenotypes, migration and type I collagen protein of VF were determined. Results showed that under the hypoxic condition, the proliferation of preadipocytes increased significantly (P<0.05), and the mRNA and protein expression of IL-6 and MCP-1 elevated markedly (P<0.05). However, the SePP1 expression reduced dramatically (P<0.05). After co-culture with VF, the VF transformed into myofibroblasts, accompanied by increased migration and elevated type I collagen expression (P<0.05). Thus, hypoxia may accumulate visceral fat and induce inflammatory state of preadipocytes, with reduced SePP1 expression, which might be involved in the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Preadipocyte; SePP1; hypoxia; interleukin 6; monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; type I collagen; vascular fibroblasts.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Hypoxic mast cells accelerate the proliferation, collagen accumulation and phenotypic alteration of human lung fibroblasts.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Jan;45(1):175-185. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4400. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31746371 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of hypoxia-pretreated rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells conditioned medium on wound healing of rats with full-thickness defects].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020 Sep 20;36(9):803-812. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20200508-00258. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32972065 Chinese.
-
Hypoxia induces leptin gene expression and secretion in human preadipocytes: differential effects of hypoxia on adipokine expression by preadipocytes.J Endocrinol. 2008 Jul;198(1):127-34. doi: 10.1677/JOE-08-0156. Epub 2008 May 7. J Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18463145
-
Angiotensin II induces monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression via a nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent pathway in rat preadipocytes.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Oct;291(4):E771-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00560.2005. Epub 2006 May 16. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16705055
-
Hypoxia reduces the response of human adipocytes towards TNFα resulting in reduced NF-κB signaling and MCP-1 secretion.Int J Obes (Lond). 2012 Jul;36(7):986-92. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2011.200. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Int J Obes (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22005720
Cited by
-
"Alphabet" Selenoproteins: Implications in Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 19;24(20):15344. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015344. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenium and Selenoproteins in Adipose Tissue Physiology and Obesity.Biomolecules. 2020 Apr 24;10(4):658. doi: 10.3390/biom10040658. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32344656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extreme Diversity of the Human Vascular Mesenchymal Cell Landscape.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Dec;9(23):e017094. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.017094. Epub 2020 Nov 16. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 33190596 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological Retrospective Study of Peritoneal Biopsies from Patients with Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis: Underestimated Role of Adipocytes as New Fibroblasts Lineage?Int J Nephrol. 2015;2015:987415. doi: 10.1155/2015/987415. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Int J Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 26366298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mostert V. Selenoprotein P: properties, functions, and regulation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000;376:433–438. - PubMed
-
- Herrmann J, Samee S, Chade A, Rodriguez Porcel M, Lerman LO, Lerman A. Differential effect of experimental hypertension and hypercholesterolemia on adventitial remodeling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:447–453. - PubMed
-
- Liu ZY, Kong W. [The role of adventitia in atherosclerosis] . Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2010;41:177–182. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
