Prevention and treatment of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in thyroid surgery
- PMID: 24482694
- PMCID: PMC3902246
Prevention and treatment of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in thyroid surgery
Abstract
Aim: To summary the experience for prevention and treatment of recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) injury in thyroid surgery.
Methods: Clinical features of 623 patients who received thyroid surgery from January 2010 to December 2012 were analyzed retrospectively, and the features of RLN injury and intraoperative as well as postoperative treatments were reviewed.
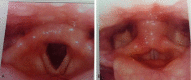
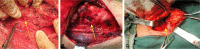
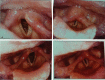
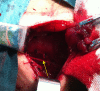
Results: RLN injury occurred in 31 patients (4.98%), in which, unilateral RLN injury occurred in 27 patients and bilateral RLN injuries occurred in 4 patients (temporary injury in 28 patients and permanent injury in 3 patients). 6 patients underwent RLN anastomosis during surgery and exhibited transient hoarseness after surgery. RLN exploration and decompression was given in 1 patient and the patient got normal vocal cord motion 2 months after surgery. 1 patient with bilateral injuries received tracheotomy and CO2 laser resection of arytenoid cartilage and achieved recovery 1 year later.
Conclusions: In order to prevent RLN injury, the anatomic variations of RLN should be mastered. Routine exposure of RLN can effectively prevent the injury in patients receiving the second or multiple surgeries. Early interventions for RLN injury include mainly early discovery, early exploration and early anastomosis, and the function of RLN in some patients can recover completely. Subsequent treatments mainly focus on the improvement of the voice, expansion of glottis and melioration of dyspnea.
Keywords: Thyroid surgery; prevention; recurrent laryngeal (RLN) injury; treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Recurrent laryngeal nerve decompression for bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve paralyses after thyroid surgery].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Nov;49(11):885-8. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25598364 Chinese.
-
[Laryngeal reinnervation for unilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve injuries caused by thyroid surgery].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2002 Aug 10;82(15):1042-5. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2002. PMID: 12194795 Chinese.
-
Recurrent laryngeal nerve identification and assessment during thyroid surgery: laryngeal palpation.World J Surg. 2004 Aug;28(8):755-60. doi: 10.1007/s00268-004-7348-x. Epub 2004 Aug 3. World J Surg. 2004. PMID: 15457354
-
Anatomical, Functional, and Dynamic Evidences Obtained by Intraoperative Neuromonitoring Improving the Standards of Thyroidectomy.Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2021 Jul 2;55(2):146-155. doi: 10.14744/SEMB.2021.45548. eCollection 2021. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2021. PMID: 34349588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Methods for the Preservation of Laryngeal Nerves During Thyroidectomy.Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2018 Jun 18;52(2):79-91. doi: 10.14744/SEMB.2018.37928. eCollection 2018. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2018. PMID: 32595378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lithium carbonate-induced giant goiter and subclinical hyperthyroidism in a patient with schizophrenia: A case report and review of literature.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Jul 16;12(20):4357-4364. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i20.4357. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39015924 Free PMC article.
-
A minimally invasive posterior lumbar interbody fusion using percutaneous long arm pedicle screw system for degenerative lumbar disease.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014 Nov 15;7(11):3964-73. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25550904 Free PMC article.
-
Contralateral recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy in revision anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF): A cautionary tale.Biomedicine (Taipei). 2021 Mar 1;11(1):51-55. doi: 10.37796/2211-8039.1114. eCollection 2021. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2021. PMID: 35223395 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular matrix deformations of the porcine recurrent laryngeal nerve in response to hydrostatic pressure.Acta Biomater. 2022 Nov;153:364-373. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.09.039. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36152909 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns and indications of intraoperative nerve monitoring usage during thyroidectomy and parathyroidectomy in Spain: results of a national survey of endocrine surgeons.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 30;14(1):17680. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68230-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39085408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akin M, Kurukahvecioglu O, Anadol AZ, Yuksel O, Taneri F. Analysis of surgical complications of thyroid diseases: results of a single institution. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2009;110:27–30. - PubMed
-
- Trésallet C, Chigot JP, Menegaux F. How to prevent recurrent nerve palsy during thyroid surgery? Ann Chir. 2006;131:149–153. - PubMed
-
- Shaw GY, Pierce E. Malpractice litigation involving iatrogenic surgical vocal fold paralysis: a closed-claims review with recommendations for prevention and management. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2009;118:6–12. - PubMed
-
- Marcus B, Edwards B, Yoo S, Byrne A, Gupta A, Kandrevas J, Bradford C, Chepeha DB, Teknos TN. Recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring in thyroid and parathyroid surgery: the University of Michigan experience. Laryngoscope. 2003;113:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Gibelin H, Sierra M, Mothes D, Ingrand P, Levillain P, Jones C, Hadjadj S, Torremocha F, Marechaud R, Barbier J, Kraimps JL. Risk factors for recurrent nodular goiter after thyroidectomy for benign disease: case-control study of 244 patients. World J Surg. 2004;28:1079–1082. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
