The Xanthomonas Ax21 protein is processed by the general secretory system and is secreted in association with outer membrane vesicles
- PMID: 24482761
- PMCID: PMC3897388
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.242
The Xanthomonas Ax21 protein is processed by the general secretory system and is secreted in association with outer membrane vesicles
Abstract
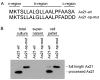
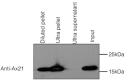
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) play an important role in detecting invading pathogens and mounting a robust defense response to restrict infection. In rice, one of the best characterized PRRs is XA21, a leucine rich repeat receptor-like kinase that confers broad-spectrum resistance to multiple strains of the bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo). In 2009 we reported that an Xoo protein, called Ax21, is secreted by a type I-secretion system and that it serves to activate XA21-mediated immunity. This report has recently been retracted. Here we present data that corrects our previous model. We first show that Ax21 secretion does not depend on the predicted type I secretion system and that it is processed by the general secretion (Sec) system. We further show that Ax21 is an outer membrane protein, secreted in association with outer membrane vesicles. Finally, we provide data showing that ax21 knockout strains do not overcome XA21-mediated immunity.
Keywords: Outer membrane vesicles; PAMPs; Plant immunity; Rice; Secretion; XA21; Xanthomonas.
Figures


References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Da Silva FG, Shen Y, Dardick C, Burdman S, Yadav RC, de Leon AL, Ronald PC. Bacterial genes involved in type I secretion and sulfation are required to elicit the rice Xa21-mediated innate immune response. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions. 2004;17:593–601. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.6.593. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dirix G, Monsieurs P, Dombrecht B, Daniels R, Marchal K, Vanderleyden J, Michiels J. Peptide signal molecules and bacteriocins in Gram-negative bacteria: a genome-wide in silico screening for peptides containing a double-glycine leader sequence and their cognate transporters. Peptides. 2004;25:1425–1440. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2003.10.028. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

