Palmitate interaction with physiological states of myoglobin
- PMID: 24482816
- PMCID: PMC3934850
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.10.028
Palmitate interaction with physiological states of myoglobin
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have shown that palmitate (PA) can bind specifically and non-specifically to Fe(III)MbCN. The present study has observed PA interaction with physiological states of Fe(II)Mb, and the observations support the hypothesis that Mb may have a potential role in facilitating intracellular fatty acid transport.
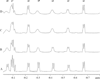
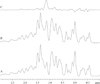
Methods: 1H NMR spectra measurements of the Mb signal during PA titration show signal changes consistent with specific and non-specific binding.
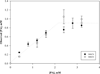
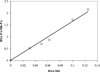
Results: Palmitate (PA) interacts differently with physiological states of Mb. Deoxy Mb does not interact specifically or non-specifically with PA, while the carbonmonoxy myoglobin (MbCO) interaction with PA decreases the intensity of selective signals and produces a 0.15ppmupfield shift of the PAmethylene peak. The selective signal change upon PA titration provides a basis to determine an apparent PA binding constant,which serves to create a model comparing the competitive PA binding and facilitated fatty acid transport of Mb and fatty acid binding protein(FABP).
Conclusions: Given contrasting PA interaction of ligated vs. unligated Mb, the cellular fatty acid binding protein(FABP) and Mb concentration in the cell, the reported cellular diffusion coefficients, the PA dissociation constants from ligated Mb and FABP, a fatty acid flux model suggests that Mb can compete with FABP transporting cellular fatty acid.
General significance: Under oxygenated conditions and continuous energy demand, Mb dependent fatty acid transport could influence the cell's preference for carbohydrate or fatty acid as a fuel source and regulate fatty acid metabolism.
Figures








References
-
- Beyer R, Fattore J. The influence of age and endurance exercise on the myoglobin concentration of skeletal muscle of the rat. Journal of Gerontology. 1984;39:525–530. - PubMed
-
- Bojesen IN, Bojesen E. Water-phase palmitate concentrations in equilibrium with albumin-bound palmitate in a biological system. J. Lipid Res. 1992;33:1327–1334. - PubMed
-
- Brooks GA, Mercier J. Balance of carbohydrate and lipid utilization during exercise: the "crossover" concept. J. Appl Physiol. 1994;76:2253–2261. - PubMed
-
- Burczynski FJ, Cai ZS. Palmitate uptake by hepatocyte suspensions: effect of albumin. Am. J. Physiol. 1994;267:G371–G379. - PubMed
-
- Burczynski FJ, Cai ZS, Moran JB, Forker EL. Palmitate uptake by cultured hepatocytes: albumin binding and stagnant layer phenomena. Am. J. Physiol. 1989;257:G584–G593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

