High sensitivity detection and quantitation of DNA copy number and single nucleotide variants with single color droplet digital PCR
- PMID: 24483992
- PMCID: PMC3982983
- DOI: 10.1021/ac403843j
High sensitivity detection and quantitation of DNA copy number and single nucleotide variants with single color droplet digital PCR
Erratum in
- Anal Chem. 2014 May 6;86(9):4635
-
Correction to High sensitivity detection and quantitation of DNA copy number and single nucleotide variants with single color droplet digital PCR.Anal Chem. 2015 Mar 3;87(5):3114. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00061. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25674918 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
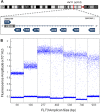
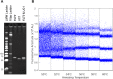
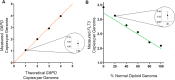
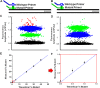
In this study, we present a highly customizable method for quantifying copy number and point mutations utilizing a single-color, droplet digital PCR platform. Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR) is rapidly replacing real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) as an efficient method of independent DNA quantification. Compared to quantative PCR, ddPCR eliminates the needs for traditional standards; instead, it measures target and reference DNA within the same well. The applications for ddPCR are widespread including targeted quantitation of genetic aberrations, which is commonly achieved with a two-color fluorescent oligonucleotide probe (TaqMan) design. However, the overall cost and need for optimization can be greatly reduced with an alternative method of distinguishing between target and reference products using the nonspecific DNA binding properties of EvaGreen (EG) dye. By manipulating the length of the target and reference amplicons, we can distinguish between their fluorescent signals and quantify each independently. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this method by examining copy number in the proto-oncogene FLT3 and the common V600E point mutation in BRAF. Using a series of well-characterized control samples and cancer cell lines, we confirmed the accuracy of our method in quantifying mutation percentage and integer value copy number changes. As another novel feature, our assay was able to detect a mutation comprising less than 1% of an otherwise wild-type sample, as well as copy number changes from cancers even in the context of significant dilution with normal DNA. This flexible and cost-effective method of independent DNA quantification proves to be a robust alternative to the commercialized TaqMan assay.
Figures

References
-
- Sykes P. J.; Neoh S. H.; Brisco M. J.; Hughes E.; Condon J.; Morley A. A. BioTechniques 1992, 13, 444. - PubMed
-
- Ottesen E. a.; Hong J. W.; Quake S. R.; Leadbetter J. R. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2006, 314, 1464. - PubMed
-
- Heyries K. A.; Tropini C.; VanInsberghe M.; Doolin C. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

