The use of 2D fingerprint methods to support the assessment of structural similarity in orphan drug legislation
- PMID: 24485002
- PMCID: PMC3923256
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-2946-6-5
The use of 2D fingerprint methods to support the assessment of structural similarity in orphan drug legislation
Abstract
Background: In the European Union, medicines are authorised for some rare disease only if they are judged to be dissimilar to authorised orphan drugs for that disease. This paper describes the use of 2D fingerprints to show the extent of the relationship between computed levels of structural similarity for pairs of molecules and expert judgments of the similarities of those pairs. The resulting relationship can be used to provide input to the assessment of new active compounds for which orphan drug authorisation is being sought.
Results: 143 experts provided judgments of the similarity or dissimilarity of 100 pairs of drug-like molecules from the DrugBank 3.0 database. The similarities of these pairs were also computed using BCI, Daylight, ECFC4, ECFP4, MDL and Unity 2D fingerprints. Logistic regression analyses demonstrated a strong relationship between the human and computed similarity assessments, with the resulting regression models having significant predictive power in experiments using data from submissions of orphan drug medicines to the European Medicines Agency. The BCI fingerprints performed best overall on the DrugBank dataset while the BCI, Daylight, ECFP4 and Unity fingerprints performed comparably on the European Medicines Agency dataset.
Conclusions: Measures of structural similarity based on 2D fingerprints can provide a useful source of information for the assessment of orphan drug status by regulatory authorities.
Figures

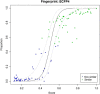
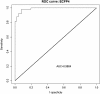
References
-
- Westermark K, Holm BB, Söderholm M, Llinares-Garcia J, Rivière F, Aarum S, Butlen-Ducuing F, Tsigkos S, Wilk-Kachlicka A, N’Diamoi C, Borvendég J, Lyons D, Sepodes B, Bloechl-Daum B, Lhoir A, Todorova M, Kkolos I, Kubáčková K, Bosch-Traberg H, Tillmann V, Saano V, Héron E, Elbers R, Siouti M, Eggenhofer J, Salmon P, Clementi M, Krieviņš D, Matulevičiene A, Metz H. et al. European regulation on orphan medicinal products: 10 years of experience and future perspectives. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10:341–349. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

