Downregulation of Smurf2, a tumor-suppressive ubiquitin ligase, in triple-negative breast cancers: involvement of the RB-microRNA axis
- PMID: 24485087
- PMCID: PMC3918234
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-57
Downregulation of Smurf2, a tumor-suppressive ubiquitin ligase, in triple-negative breast cancers: involvement of the RB-microRNA axis
Abstract
Background: The HECT family ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 regulates cell polarity, migration, division, differentiation and death, by targeting diverse substrates that are critical for receptor signaling, cytoskeleton, chromatin remodeling and transcription. Recent studies suggest that Smurf2 functions as a tumor suppressor in mice. However, no inactivating mutation of SMURF2 has been reported in human, and information about Smurf2 expression in human cancer remains limited or complicated. Here we demonstrate that Smurf2 expression is downregulated in human breast cancer tissues, especially of the triple-negative subtype, and address the mechanism of Smurf2 downregulation in triple-negative breast cancer cells.
Methods: Human breast cancer tissues (47 samples expressing estrogen receptor (ER) and 43 samples with triple-negative status) were examined by immunohistochemistry for the expression of Smurf2. Ten widely-studied human breast cancer cell lines were examined for the expression of Smurf2. Furthermore, microRNA-mediated regulation of Smurf2 was investigated in triple-negative cancer cell lines.
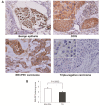
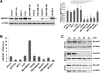
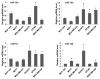
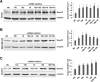
Results: Immunohistochemical analysis showed that benign mammary epithelial cells expressed high levels of Smurf2, so did cells in ductal carcinomas in situ. In contrast, invasive ductal carcinomas showed focal or diffuse decrease in Smurf2 expression, which was observed more frequently in triple-negative tumors than in ER-positive tumors. Consistently, human triple-negative breast cancer cell lines such as BT549, MDA-MB-436, DU-4475 and MDA-MB-468 cells showed significantly lower expression of Smurf2 protein, compared to ER + or HER2+ cell lines. Studies using quantitative PCR and specific microRNA inhibitors indicated that increased expression of miR-15a, miR-15b, miR-16 and miR-128 was involved in Smurf2 downregulation in those triple-negative cancer cell lines, which have mutations in the retinoblastoma (RB) gene. Forced expression of RB increased levels of Smurf2 protein with concomitant decreases in the expression of the microRNAs.
Conclusions: This study provides evidence of posttranscriptional downregulation of Smurf2 in triple-negative breast cancers, and demonstrates that the loss of RB function is involved in microRNA-mediated interference with Smurf2 translation. The new link from RB inactivation to Smurf2 downregulation is likely to play a role in malignant phenotypes of triple-negative breast cancer cells.
Figures
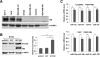
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of ligase defective E6-associated protein, E6-AP, results in mammary tumorigenesis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Feb;132(1):97-108. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1567-2. Epub 2011 May 8. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21553290
-
Keratin 17 is overexpressed and predicts poor survival in estrogen receptor-negative/human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer.Hum Pathol. 2017 Apr;62:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Hum Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27816721
-
Regulation of CNKSR2 protein stability by the HECT E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf2, and its role in breast cancer progression.BMC Cancer. 2018 Mar 13;18(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4188-x. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29534682 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoblastoma tumor suppressor pathway in breast cancer: prognosis, precision medicine, and therapeutic interventions.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 May 7;16(3):207. doi: 10.1186/bcr3652. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25223380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From microRNA functions to microRNA therapeutics: novel targets and novel drugs in breast cancer research and treatment (Review).Int J Oncol. 2013 Oct;43(4):985-94. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2059. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23939688 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA: master controllers of intracellular signaling pathways.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Sep;72(18):3531-42. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1940-0. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26059472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges for Super-Resolution Localization Microscopy and Biomolecular Fluorescent Nano-Probing in Cancer Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 28;18(10):2066. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102066. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28956810 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the epigenetic code: new insights into triple-negative breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 18;14:1499950. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1499950. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39744000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smurfs in Protein Homeostasis, Signaling, and Cancer.Front Oncol. 2018 Aug 2;8:295. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00295. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30116722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orthogonal ubiquitin transfer identifies ubiquitination substrates under differential control by the two ubiquitin activating enzymes.Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 30;8:14286. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14286. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28134249 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morris GJ, Naidu S, Topham AK, Guiles F, Xu Y, McCue P, Schwartz GF, Park PK, Rosenberg AL, Brill K. et al.Differences in breast carcinoma characteristics in newly diagnosed African-American and Caucasian patients: a single-institution compilation compared with the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. Cancer. 2007;110:876–884. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22836. - DOI - PubMed
-
- David D, Nair SA, Pillai MR. Smurf E3 ubiquitin ligases at the cross roads of oncogenesis and tumor suppression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1835;2013:119–128. - PubMed
-
- Fukuchi M, Fukai Y, Masuda N, Miyazaki T, Nakajima M, Sohda M, Manda R, Tsukada K, Kato H, Kuwano H. High-level expression of the Smad ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 correlates with poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Canc Res. 2002;62:7162–7165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

