d-Cycloserine augmentation of cognitive remediation in schizophrenia
- PMID: 24485587
- PMCID: PMC4547356
- DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.01.016
d-Cycloserine augmentation of cognitive remediation in schizophrenia
Abstract
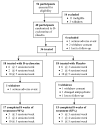
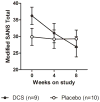
d-Cycloserine (DCS) has been shown to enhance memory and, in a previous trial, once-weekly DCS improved negative symptoms in schizophrenia subjects. We hypothesized that DCS combined with a cognitive remediation (CR) program would improve memory of a practiced auditory discrimination task and that gains would generalize to performance on unpracticed cognitive tasks. Stable, medicated adult schizophrenia outpatients participated in the Brain Fitness CR program 3-5 times per week for 8weeks. Subjects were randomly assigned to once-weekly adjunctive treatment with DCS (50mg) or placebo administered before the first session each week. Primary outcomes were performance on an auditory discrimination task, the MATRICS cognitive battery composite score and the Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS) total score. 36 subjects received study drug and 32 completed the trial (average number of CR sessions=26.1). Performance on the practiced auditory discrimination task significantly improved in the DCS group compared to the placebo group. DCS was also associated with significantly greater negative symptom improvement for subjects symptomatic at baseline (SANS score ≥20). However, improvement on the MATRICS battery was observed only in the placebo group. Considered with previous results, these findings suggest that DCS augments CR and alleviates negative symptoms in schizophrenia patients. However, further work is needed to evaluate whether CR gains achieved with DCS can generalize to other unpracticed cognitive tasks.
Keywords: Cognitive remediation; MATRICS; Memory; SANS; Schizophrenia; d-Cycloserine.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
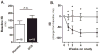
Similar articles
-
Once-weekly D-cycloserine effects on negative symptoms and cognition in schizophrenia: an exploratory study.Schizophr Res. 2008 Dec;106(2-3):320-7. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2008.08.012. Epub 2008 Sep 16. Schizophr Res. 2008. PMID: 18799288 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Cognitive and Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia Trial (CONSIST): the efficacy of glutamatergic agents for negative symptoms and cognitive impairments.Am J Psychiatry. 2007 Oct;164(10):1593-602. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.06081358. Am J Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17898352 Clinical Trial.
-
D-cycloserine augmentation of cognitive behavioral therapy for delusions: A randomized clinical trial.Schizophr Res. 2020 Aug;222:145-152. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2020.06.015. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Schizophr Res. 2020. PMID: 32591238 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of D-cycloserine on negative symptoms in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2004 Dec 1;71(2-3):239-48. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2004.03.013. Schizophr Res. 2004. PMID: 15474895 Review.
-
The Therapeutic Role of d-Cycloserine in Schizophrenia.Adv Pharmacol. 2016;76:39-66. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Adv Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27288073 Review.
Cited by
-
Drugs Based on NMDAR Hypofunction Hypothesis in Schizophrenia.Front Neurosci. 2021 Apr 12;15:641047. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.641047. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33912003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
D-cycloserine in Schizophrenia: New Strategies for Improving Clinical Outcomes by Enhancing Plasticity.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(1):21-34. doi: 10.2174/1570159x14666160225154812. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017. PMID: 26915421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Neuropsychological Profile and Working Memory in Bipolar Disorder].Can J Psychiatry. 2018 May;63(5):314-321. doi: 10.1177/0706743717744777. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Can J Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29186974 Free PMC article. French.
-
A randomized controlled trial of cognitive remediation and d-cycloserine for individuals with bipolar disorder.BMC Psychol. 2014 Oct 10;2(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s40359-014-0041-4. eCollection 2014. BMC Psychol. 2014. PMID: 25566387 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Augmenting N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Signaling on Working Memory and Experience-Dependent Plasticity in Schizophrenia: An Exploratory Study Using Acute d-cycloserine.Schizophr Bull. 2017 Sep 1;43(5):1123-1133. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbw193. Schizophr Bull. 2017. PMID: 28338977 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bailey JE, Papadopoulos A, Lingford-Hughes A, Nutt DJ. D-Cycloserine and performance under different states of anxiety in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2007;193(4):579–585. - PubMed
-
- Beneyto M, Meador-Woodruff JH. Lamina-specific abnormalities of NMDA receptor-associated postsynaptic protein transcripts in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33(9):2175–2186. - PubMed
-
- Buchanan RW, Javitt DC, Marder SR, Schooler NR, Gold JM, McMahon RP, Heresco-Levy U, Carpenter WT. The Cognitive and Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia Trial (CONSIST): the efficacy of glutamatergic agents for negative symptoms and cognitive impairments. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(10):1593–1602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

