The Refractory Overactive Bladder: Sacral NEuromodulation vs. BoTulinum Toxin Assessment: ROSETTA trial
- PMID: 24486637
- PMCID: PMC3989885
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2014.01.009
The Refractory Overactive Bladder: Sacral NEuromodulation vs. BoTulinum Toxin Assessment: ROSETTA trial
Abstract
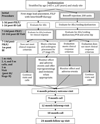
We present the rationale for and design of a randomized, open-label, active-control trial comparing the effectiveness of 200 units of onabotulinum toxin A (Botox A®) versus sacral neuromodulation (InterStim®) therapy for refractory urgency urinary incontinence (UUI). The Refractory Overactive Bladder: Sacral NEuromodulation vs. BoTulinum Toxin Assessment (ROSETTA) trial compares changes in urgency urinary incontinence episodes over 6 months, as well as other lower urinary tract symptoms, adverse events and cost effectiveness in women receiving these two therapies. Eligible participants had previously attempted treatment with at least 2 medications and behavioral therapy. We discuss the importance of evaluating two very different interventions, the challenges related to recruitment, ethical considerations for two treatments with significantly different costs, follow-up assessments and cost effectiveness. The ROSETTA trial will provide information to healthcare providers regarding the technical attributes of these interventions as well as the efficacy and safety of these two interventions on other lower urinary tract and pelvic floor symptoms. Enrollment began in March, 2012 with anticipated end to recruitment in mid 2014.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01502956.
Keywords: Onabotulinum toxin A; Sacral neuromodulation; Urgency urinary incontinence.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart WF, Van Rooyen JB, Cundiff GW, Abrams P, Herzog AR, Corey R, et al. Prevalence and burden of overactive bladder in the United States. World J Urol. 2003;20:327–336. - PubMed
-
- Amundsen CL, Romero AA, Jamison MG, Webster GD. Sacral neuromodulation for intractable urge incontinence: are there factors associated with cure? Urology. 2005;66:746–750. - PubMed
-
- Rajkumar GN, Small DR, Mustafa AW, Conn G. A prospective study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, efficacy and durability of response of intravesical injection of botulinum toxin type A into detrusor muscle in patients with refractory idiopathic detrusor overactivity. BJU Int. 2005;96:848–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 HD069031/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041261/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD054215/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD054214/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD069031/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041267/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD041267/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD054241/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041250/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10-HD041267/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD069010/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD069006/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD069010/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HD069031/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD054241/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases