Immunologic response to the survivin-derived multi-epitope vaccine EMD640744 in patients with advanced solid tumors
- PMID: 24487961
- PMCID: PMC11029529
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-013-1516-5
Immunologic response to the survivin-derived multi-epitope vaccine EMD640744 in patients with advanced solid tumors
Abstract
Purpose: Survivin is a member of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis family. Essential for tumor cell survival and overexpressed in most cancers, survivin is a promising target for anti-cancer immunotherapy. Immunogenicity has been demonstrated in multiple cancers. Nonetheless, few clinical trials have demonstrated survivin-vaccine-induced immune responses.
Experimental design: This phase I trial was conducted to test whether vaccine EMD640744, a cocktail of five HLA class I-binding survivin peptides in Montanide(®) ISA 51 VG, promotes anti-survivin T-cell responses in patients with solid cancers. The primary objective was to compare immunologic efficacy of EMD640744 at doses of 30, 100, and 300 μg. Secondary objectives included safety, tolerability, and clinical efficacy.
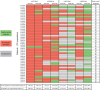
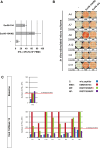
Results: In total, 49 patients who received ≥2 EMD640744 injections with available baseline- and ≥1 post-vaccination samples [immunologic-diagnostic (ID)-intention-to-treat] were analyzed by ELISpot- and peptide/MHC-multimer staining, revealing vaccine-activated peptide-specific T-cell responses in 31 patients (63 %). This cohort included the per study protocol relevant ID population for the primary objective, i.e., T-cell responses by ELISpot in 17 weeks following first vaccination, as well as subjects who discontinued the study before week 17 but showed responses to the treatment. No dose-dependent effects were observed. In the majority of patients (61 %), anti-survivin responses were detected only after vaccination, providing evidence for de novo induction. Best overall tumor response was stable disease (28 %). EMD640744 was well tolerated; local injection-site reactions constituted the most frequent adverse event.
Conclusions: Vaccination with EMD640744 elicited T-cell responses against survivin peptides in the majority of patients, demonstrating the immunologic efficacy of EMD640744.
Conflict of interest statement
Juergen Zieschang is a Merck employee. Ulf Forssmann was a Merck employee until the end of March 2013. Ulrike Gnad-Vogt was a Merck employee from 2005 to 2009 and received consultancy fees and a travel grant from Merck from 2009 to 2011 and has been a CureVac GmbH employee since 2011. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Velculescu VE, Madden SL, Zhang L, Lash AE, Yu J, Rago C, Lal A, Wang CJ, Beaudry GA, Ciriello KM, Cook BP, Dufault MR, Ferguson AT, Gao Y, He TC, Hermeking H, Hiraldo SK, Hwang PM, Lopez MA, Luderer HF, Mathews B, Petroziello JM, Polyak K, Zawel L, Kinzler KW, et al. Analysis of human transcriptomes. Nat Genet. 1999;23(4):387–388. doi: 10.1038/70487. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Satoh K, Kaneko K, Hirota M, Masamune A, Satoh A, Shimosegawa T. Expression of survivin is correlated with cancer cell apoptosis and is involved in the development of human pancreatic duct cell tumors. Cancer. 2001;92(2):271–278. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(20010715)92:2<271::AID-CNCR1319>3.0.CO;2-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

