EphA2 promotes infiltrative invasion of glioma stem cells in vivo through cross-talk with Akt and regulates stem cell properties
- PMID: 24488013
- PMCID: PMC4119862
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2013.590
EphA2 promotes infiltrative invasion of glioma stem cells in vivo through cross-talk with Akt and regulates stem cell properties
Abstract
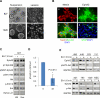
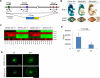
Diffuse infiltrative invasion is a major cause for the dismal prognosis of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), but the underlying mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Using human glioma stem cells (GSCs) that recapitulate the invasive propensity of primary GBM, we find that EphA2 critically regulates GBM invasion in vivo. EphA2 was expressed in all seven GSC lines examined, and overexpression of EphA2 enhanced intracranial invasion. The effects required Akt-mediated phosphorylation of EphA2 on serine 897. In vitro the Akt-EphA2 signaling axis is maintained in the absence of ephrin-A ligands and is disrupted upon ligand stimulation. To test whether ephrin-As in tumor microenvironment can regulate GSC invasion, the newly established Efna1;Efna3;Efna4 triple knockout mice (TKO) were used in an ex vivo brain slice invasion assay. We observed significantly increased GSC invasion through the brain slices of TKO mice relative to wild-type (WT) littermates. Mechanistically EphA2 knockdown suppressed stem cell properties of GSCs, causing diminished self-renewal, reduced stem marker expression and decreased tumorigenicity. In a subset of GSCs, the reduced stem cell properties were associated with lower Sox2 expression. Overexpression of EphA2 promoted stem cell properties in a kinase-independent manner and increased Sox2 expression. Disruption of Akt-EphA2 cross-talk attenuated stem cell marker expression and neurosphere formation while having minimal effects on tumorigenesis. Taken together, the results show that EphA2 endows invasiveness of GSCs in vivo in cooperation with Akt and regulates glioma stem cell properties.
Figures




References
-
- Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007 Nov 1;21(21):2683–710. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009 May;10(5):459–66. - PubMed
-
- Chakravarti A, Palanichamy K. Overcoming therapeutic resistance in malignant gliomas: current practices and future directions. Cancer Treat Res. 2008;139:173–89. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose S, Wang SI, et al. PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer [see comments]. Science. 1997;275(5308):1943–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

