The granzyme B-Serpinb9 axis controls the fate of lymphocytes after lysosomal stress
- PMID: 24488096
- PMCID: PMC4013521
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2014.7
The granzyme B-Serpinb9 axis controls the fate of lymphocytes after lysosomal stress
Abstract
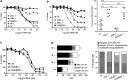
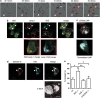
Cytotoxic lymphocytes (CLs) contain lysosome-related organelles (LROs) that perform the normal degradative functions of the lysosome, in addition to storage and release of powerful cytotoxins employed to kill virally infected or abnormal cells. Among these cytotoxins is granzyme B (GrB), a protease that has also been implicated in activation (restimulation)-induced cell death of natural killer (NK) and T cells, but the underlying mechanism and its regulation are unclear. Here we show that restimulation of previously activated human or mouse lymphocytes induces lysosomal membrane permeabilisation (LMP), followed by GrB release from LROs into the CL cytosol. The model lysosomal stressors sphingosine and Leu-Leu-methyl-ester, and CLs from gene-targeted mice were used to show that LMP releases GrB in both a time- and concentration-dependent manner, and that the liberated GrB is responsible for cell death. The endogenous GrB inhibitor Serpinb9 (Sb9) protects CLs against LMP-induced death but is decreasingly effective as the extent of LMP increases. We also used these model stressors to show that GrB is the major effector of LMP-mediated death in T cells, but that in NK cells additional effectors are released, making GrB redundant. We found that limited LMP and GrB release occurs constitutively in proliferating lymphocytes and in NK cells engaged with targets in vitro. In Ectromelia virus-infected lymph nodes, working NK cells lacking Sb9 are more susceptible to GrB-mediated death. Taken together, these data show that a basal level of LMP occurs in proliferating and activated lymphocytes, and is increased on restimulation. LMP releases GrB from LROs into the lymphocyte cytoplasm and its ensuing interaction with Sb9 dictates whether or not the cell survives. The GrB-Sb9 nexus may therefore represent an additional mechanism of limiting lymphocyte lifespan and populations.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The biological function of Serpinb9 and Serpinb9-based therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 20;15:1422113. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1422113. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38966643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Serpin Regulatory Mechanism: SerpinB9 IS REVERSIBLY INHIBITED BY VICINAL DISULFIDE BOND FORMATION IN THE REACTIVE CENTER LOOP.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 12;291(7):3626-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.699298. Epub 2015 Dec 15. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26670609 Free PMC article.
-
Serpinb9 (Spi6)-deficient mice are impaired in dendritic cell-mediated antigen cross-presentation.Immunol Cell Biol. 2012 Oct;90(9):841-51. doi: 10.1038/icb.2012.29. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22801574
-
Intracellular serine protease inhibitor SERPINB4 inhibits granzyme M-induced cell death.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022645. Epub 2011 Aug 3. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21857942 Free PMC article.
-
Granzyme B-induced apoptosis in cancer cells and its regulation (review).Int J Oncol. 2010 Dec;37(6):1361-78. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000788. Int J Oncol. 2010. PMID: 21042704 Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction Networks Converging on Immunosuppressive Roles of Granzyme B: Special Niches Within the Tumor Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 1;12:670324. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.670324. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biological function of Serpinb9 and Serpinb9-based therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 20;15:1422113. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1422113. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38966643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomics of Acute DENV-Specific CD8+ T Cells Does Not Support Qualitative Differences as Drivers of Disease Severity.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Apr 14;10(4):612. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10040612. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455361 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Serpin Regulatory Mechanism: SerpinB9 IS REVERSIBLY INHIBITED BY VICINAL DISULFIDE BOND FORMATION IN THE REACTIVE CENTER LOOP.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 12;291(7):3626-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.699298. Epub 2015 Dec 15. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26670609 Free PMC article.
-
A pro-survival role for the intracellular granzyme B inhibitor Serpinb9 in natural killer cells during poxvirus infection.Immunol Cell Biol. 2017 Nov;95(10):884-894. doi: 10.1038/icb.2017.59. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28722018
References
-
- Brenner D, Golks A, Becker M, Muller W, Frey CR, Novak R, et al. Caspase-cleaved HPK1 induces CD95L-independent activation-induced cell death in T and B lymphocytes. Blood. 2007;110:3968–3977. - PubMed
-
- Chhabra A, Mehrotra S, Chakraborty NG, Dorsky DI, Mukherji B. Activation-induced cell death of human melanoma specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes is mediated by apoptosis-inducing factor. Eur J Immunol. 2006;36:3167–3174. - PubMed
-
- Ida H, Robertson MJ, Voss S, Ritz J, Anderson P. CD94 ligation induces apoptosis in a subset of IL-2-stimulated NK cells. J Immunol. 1997;159:2154–2160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

